AWS RDS Instance Observability in DDI Central
AWS RDS Instance Observability in DDI Central
Amazon RDS (Relational Database Service) is a managed database platform that simplifies the deployment and scaling of databases like MySQL, PostgreSQL, SQL Server, and more. It abstracts infrastructure complexities like backups, patching, and high availability, allowing teams to focus on application logic.
But for network admins, RDS instances can be black boxes—hard to map, track, or troubleshoot within sprawling hybrid environments.
How DDI Central's Cloud Observability Makes a Difference:
With DDI Central’s RDS integration, network admins gain context-rich visibility across every IP-connected database resource in AWS:
- See Where RDS Lives: View every instance’s availability zone, VPC, and subnet mapping at a glance. This aids in AZ planning, fault tolerance, and routing design.
- Track IP Assignments: Understand backend IP usage to reduce conflicts and improve DNS naming schemes.
- Validate DNS Routing: Ensure DNS records correctly reflect the RDS footprint and that application-level failovers are resolvable via DNS.
- Troubleshoot Faster: Identify missing, failed, or misaligned RDS resources in the service chain that could be breaking application performance.
- Audit and Optimize: Get a complete inventory with state, engine type, and IP-to-resource correlation to streamline network audits and capacity planning.
DDI Central turns RDS infrastructure into a fully transparent and manageable network entity, helping busy admins:
- Troubleshoot faster
- Design more resilient services
- Maintain clean, conflict-free IP and DNS plans
- All without needing deep cloud console dives or switching tools.
To access and analyze RDS resources within DDI Central
- Log into DDI Central using the web UI. Only an Admin or Operator with pertinent access privileges to a cloud cluster can access a Cloud Observability cluster.
- Select an AWS-integrated Cloud Observability Cluster, created during cloud integration setup, from the top right corner within the Web UI.
- Navigate to IPAM → RDS menu inside the selected cluster.
- Select the Availability Zone of your choice. The DB Clusters in the chosen region will be listed. Choose the DB Cluster of your choice. DDI Central will display a dedicated dashboard for the AWS RDS instance observability. This dashboard helps admins gain in-depth visibility into Amazon RDS deployment across multi-AZ environments. It unifies database service discovery, subnet mapping, and operational posture monitoring into one centralized interface.
Global DB Instance Overview
Service Availability Map (Country-Wise)
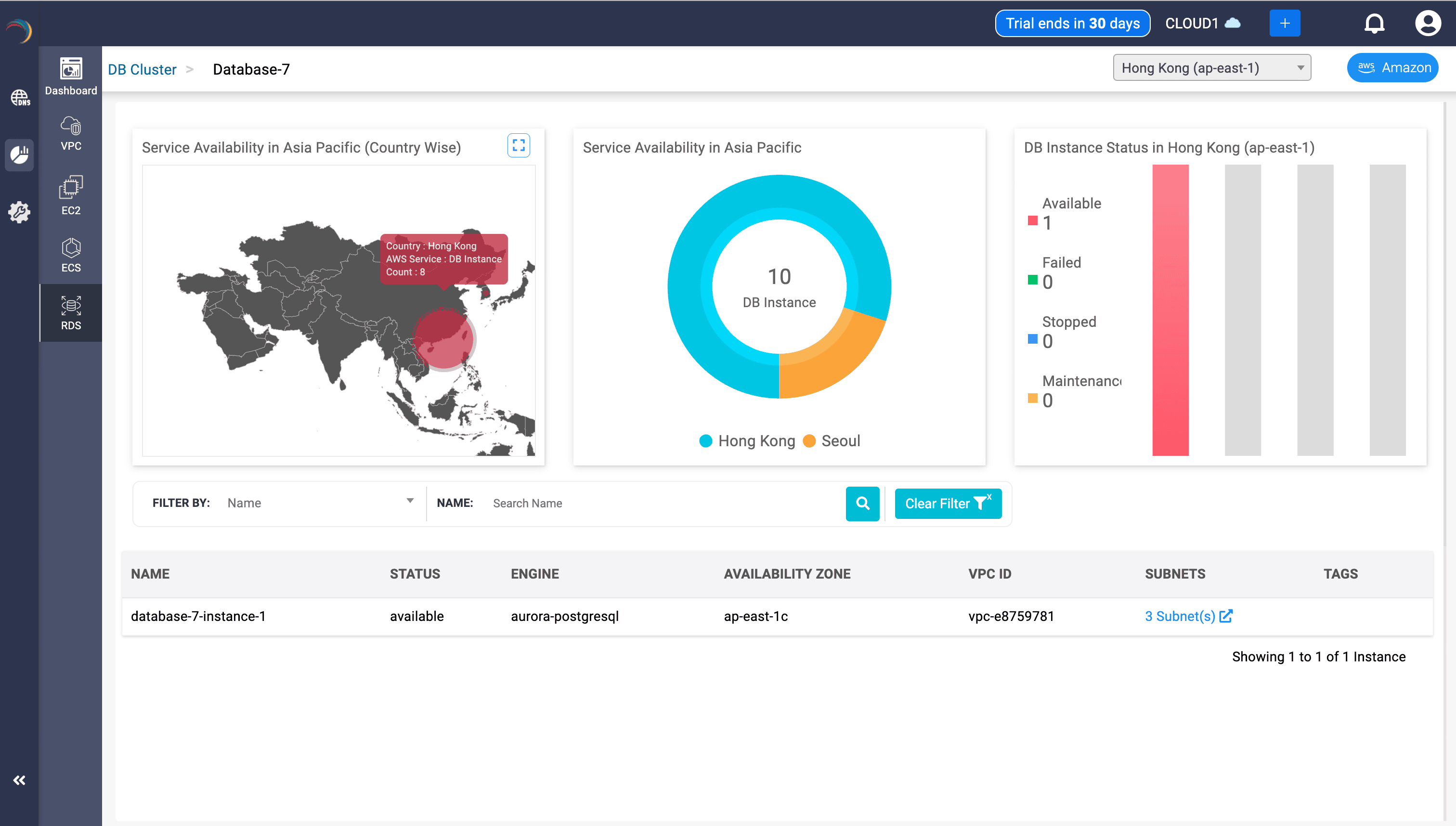
- A dynamic world map showing the geographic footprint of RDS deployments.
- Highlights:
- Circle size corresponds to DB instance count per country (e.g., 8 in Hong Kong).
- Hover reveals country name, AWS service, and instance count.
- Offers geographic insights into DB instance sprawl, helping with latency-aware application design, failover planning, and data residency audits.
Regional Donut Chart
- Graphical representation of DB instance count segmented by region.
- Helps validate regional clustering strategy, ensuring high availability across AZs.
DB Instance Status Graph (Bar Chart)
- Status breakdown of DB instances by state (e.g., Available, Failed, Stopped, Maintenance).
- Provides instant infrastructure health snapshot to assess DB availability.
6. RDS Instance Inventory Table
Instance Metadata Columns
- Fields:
- Name: Logical DB instance identifier (e.g., database-7-instance-1)
- Status: Current operational state (e.g., Available)
- Engine: DB engine type (e.g., aurora-postgresql)
- Availability Zone: Host AZ (e.g., ap-east-1c)
- VPC ID: Tenant VPC hosting the RDS instance
- Subnets: Number and drilldown into associated subnets
- Allows a holistic view of deployed DB engines, their operational status, and tenancy mapping for security boundary tracing and compliance.
7. Subnet Drilldown Modal
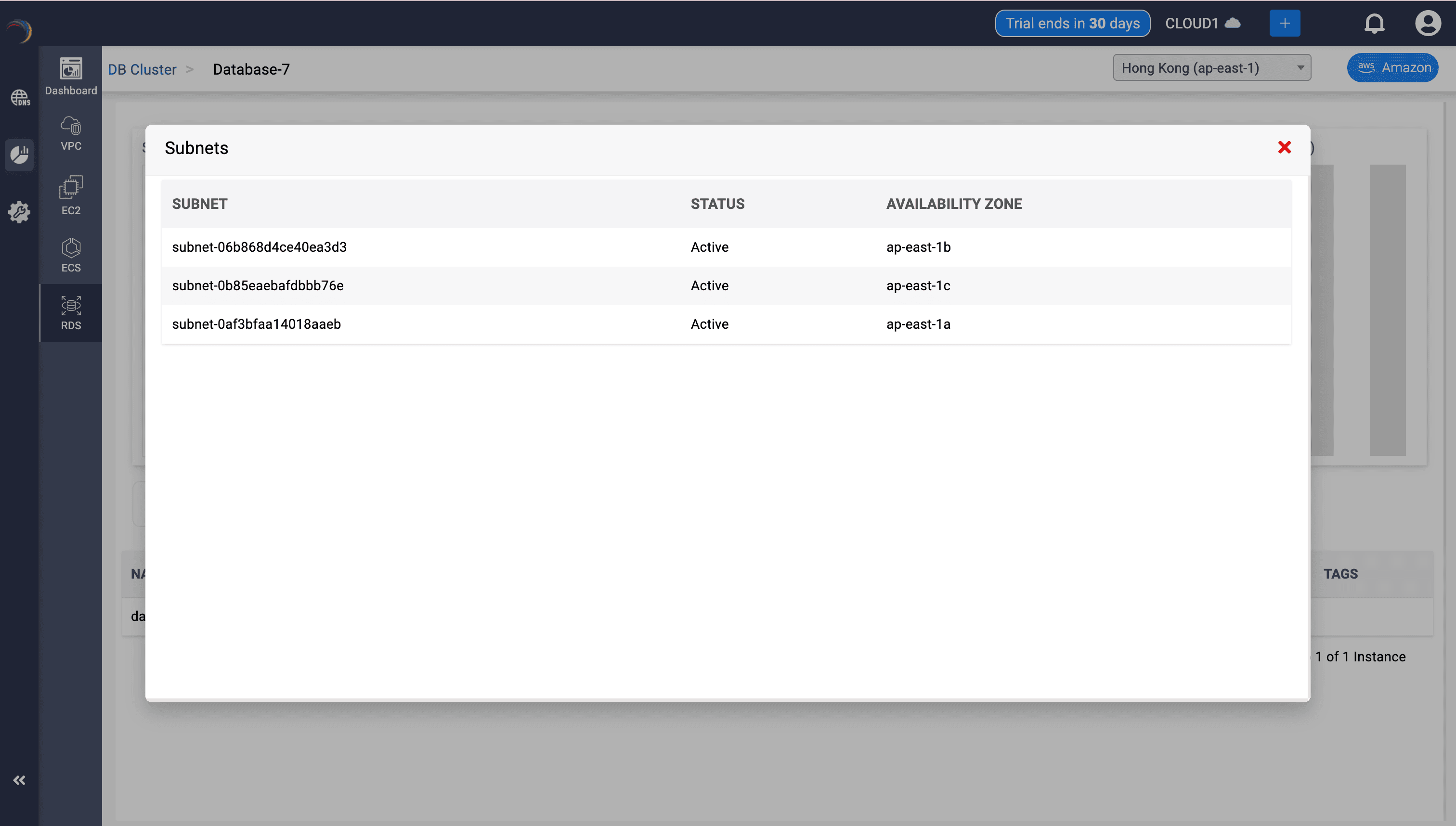
Subnet Association Breakdown
- Details:
- Subnet IDs: Unique identifiers for each associated subnet.
- Status: Operational state of subnet (e.g., Active)
- Availability Zone: AZ coverage (e.g., ap-east-1a, 1b, 1c)
- Crucial for ensuring AZ redundancy, verifying DB failover coverage, and subnet-based routing enforcement.
Why It's Effective
With DDI Central RDS observability, administrators can:
- Track DB engine types and health across AZs and countries
- Validate HA policies with subnet spread verification
- Cross-link RDS instances to VPC and subnet identities
- Use regional analytics to optimize DB deployment strategy
- Reduce MTTI (Mean Time to Identify) for failures through visual cues
- DDI Central empowers your team with rich RDS service observability—unifying networking and database context under one intelligent console.
New to ADSelfService Plus?
Related Articles
AWS Integration with DDI Central
AWS Integration with DDI Central DDI Central seamlessly integrates with Amazon Web Services (AWS) to provide deep visibility and centralized oversight of key cloud infrastructure components— EC2 instances, ECS services, RDS databases, VPCs, and their ...AWS Integration Dashboard in DDI Central
AWS Integration Dashboard in DDI Central DDI Central’s AWS integration dashboard provides network administrators a centralized, visual snapshot of their AWS resource landscape across VPC, EC2, ECS, and RDS services. This guide outlines how to ...Analyzing AWS VPCs and VPC Subnets in DDI Central
Analyzing AWS VPCs and VPC Subnets in DDI Central Table of Contents Analyzing AWS VPC VPC: Subnets VPC: Instances VPC: Network Interfaces VPC: Load Balanceers VPC: DB Instances Analyzing AWS Subnets within VPCs VPC Subnets: VPC VPC Subnets: Instances ...DDI Central for Microsoft DNS DHCP
About ManageEngine DDI Central DDI Central is a comprehensive network management solution that unifies DNS, DHCP, and IP Address Management (IPAM) to enhance operational efficiency and network stability. It is deployed as an overlay on your existing ...Cloud Observability in DDI Central
Cloud Observability in DDI Central For Unified Visibility Across Cloud Networks As enterprises expand their cloud footprint, network teams are often left grappling with fragmented visibility across platforms, resources, and services. DDI Central’s ...