Configuring DNS Records
Configuring DNS Records
DNS records hold information about domain names, and their associated properties and behaviour. They are stored in authoritative DNS servers and consist of a series of text files written in DNS syntax, a string of characters that directs the DNS server on what and how to respond to DNS queries.
Types of DNS Records
There are various types of DNS records in DNS zones, and each one has a different use.
What is an A record
An A record is the most commonly used record and is required as its primary purpose is to map out the Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) to the respective IPv4 address. They are mostly used for DNS lookups.
A records can also be used for pointing to a subdomain which also contains the same IP address.
How do you create an A record?
Step 1: On the Domains page, click on a domain name of your choice to access its records. Navigate to the A record section.
Step 2: On the right side, you can view a "+" sign for adding a record, and a "-" sign for deleting a record. Click the "+" sign to add a new A record.
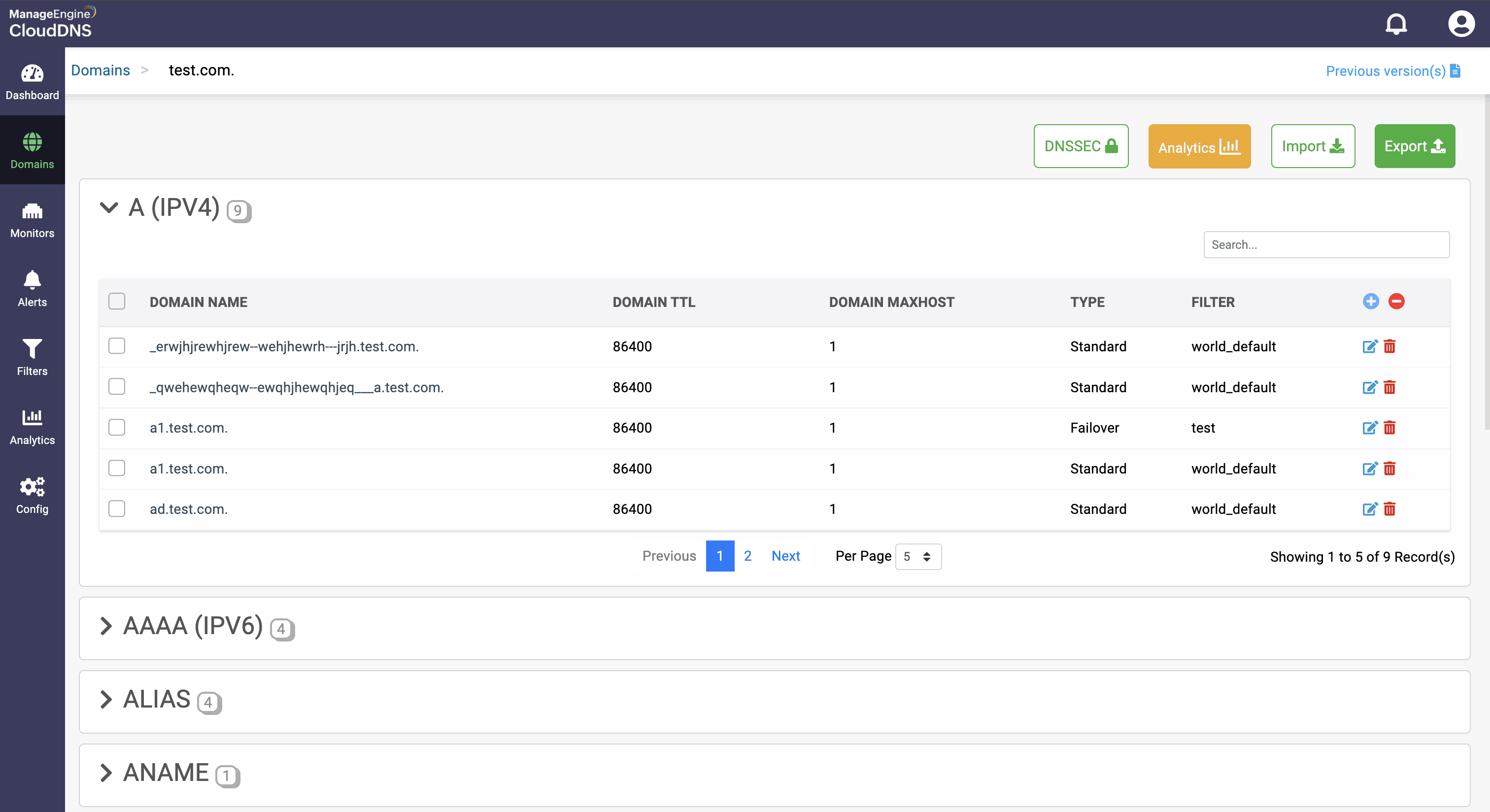
Step 3: Provide the details of the new A record, such as name, TTL, date and time, and IP address.
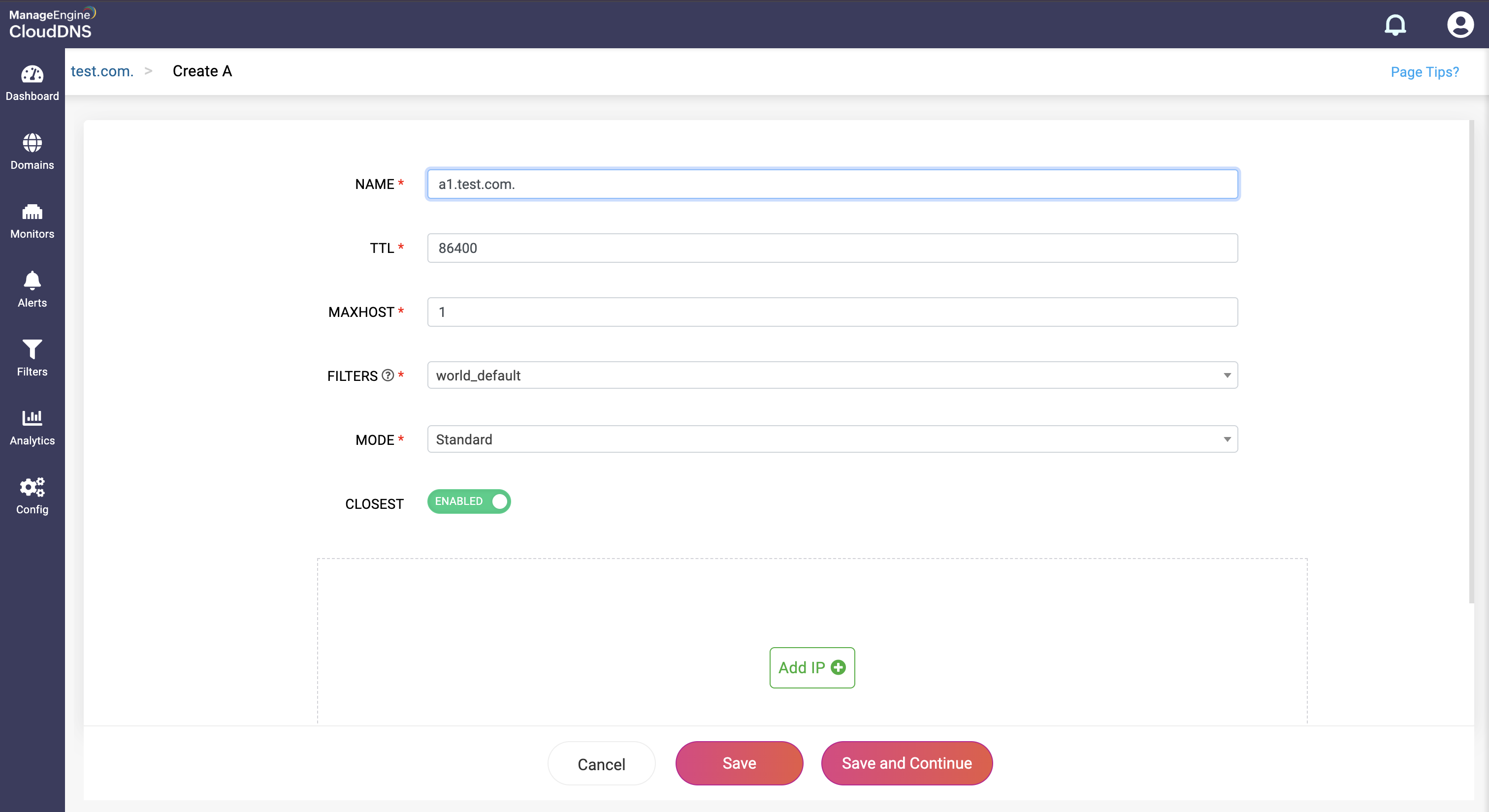
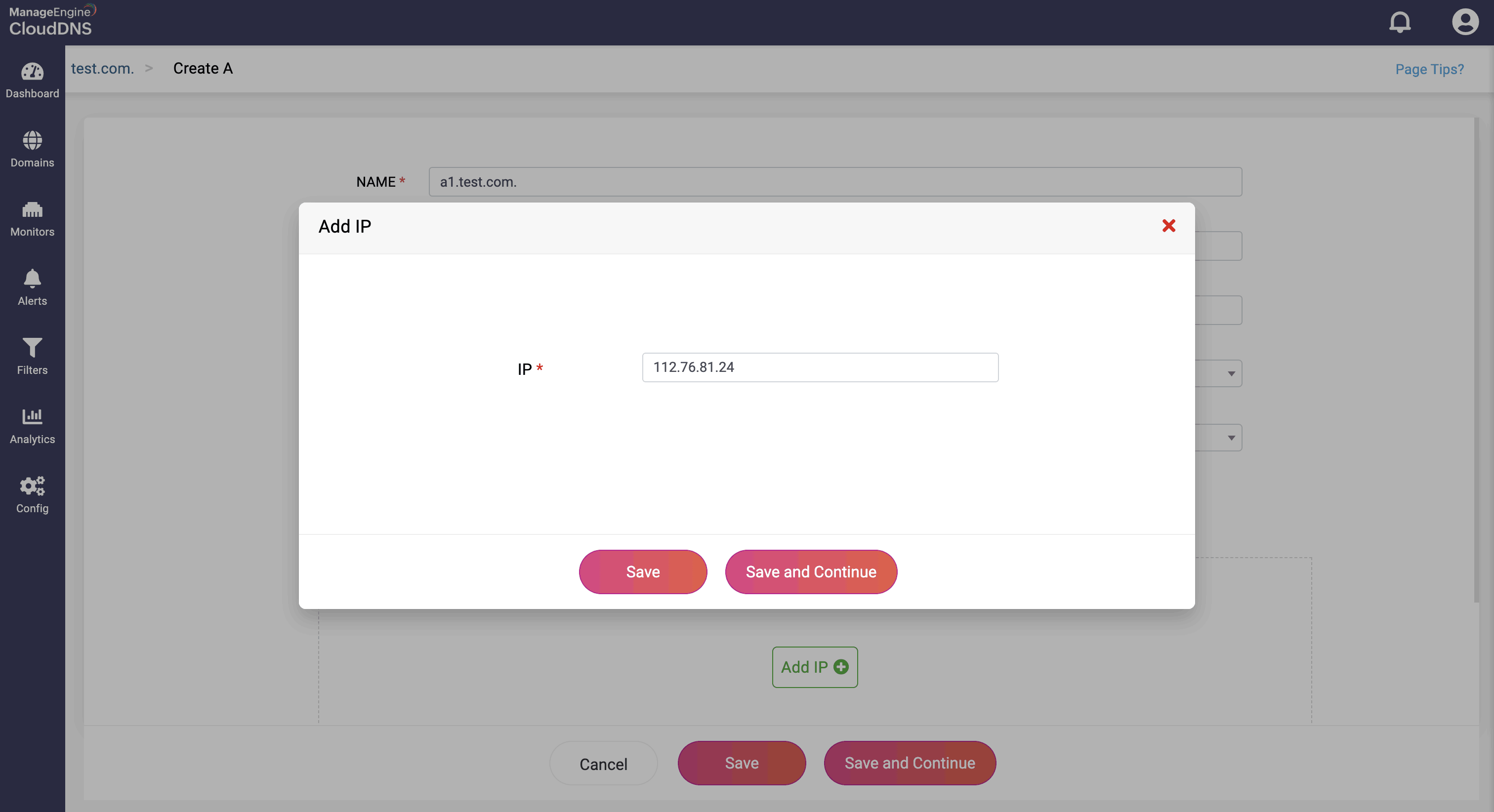
Step 4: Proceed to save the record by clicking on "Save" or "Save and Continue" to keep adding more entries to the record.
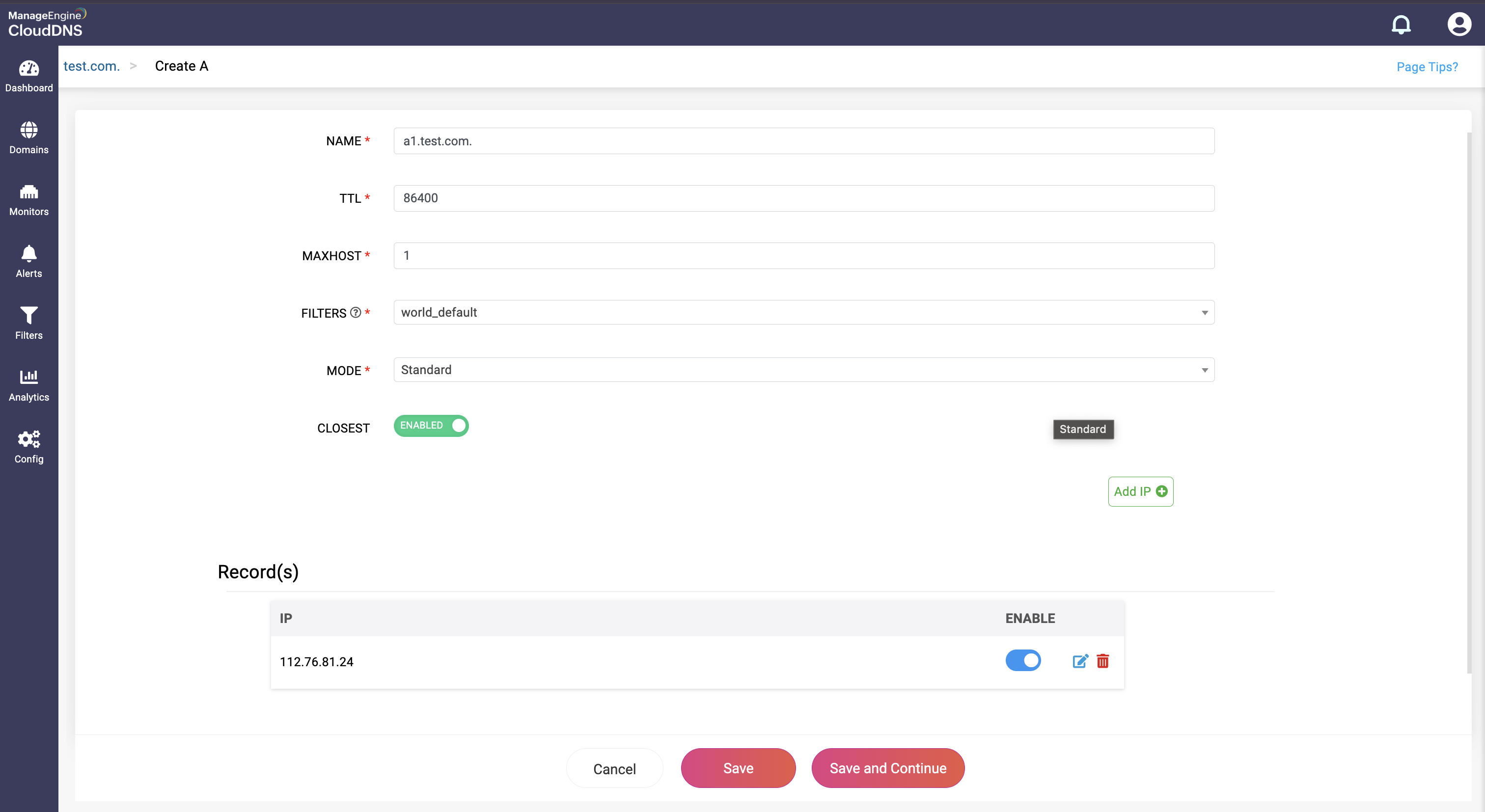
What is an AAAA DNS record
AAAA records, also know as quad A records, is also required but are primarily used for mapping out the domain name to an IPv6 address. An AAAA record serves the same purpose as the A record, except that the A record has IPv4 addresses, while AAAA record has IPv6 addresses.
They are mostly used for DNS lookups for domain names requiring IPv6 addresses. AAAA records are needed for the latest domains created which support IPv6 as the number of domains supporting IPv4 are diminishing.
How do you create an AAAA record?
Step 1: On the Domains page, click on a domain name of your choice to access its records. Navigate to the AAAA record section.
Step 2: On the right side, you can view a "+" sign for adding a record, and a "-" sign for deleting a record. Click the "+" sign to add a new AAAA record.
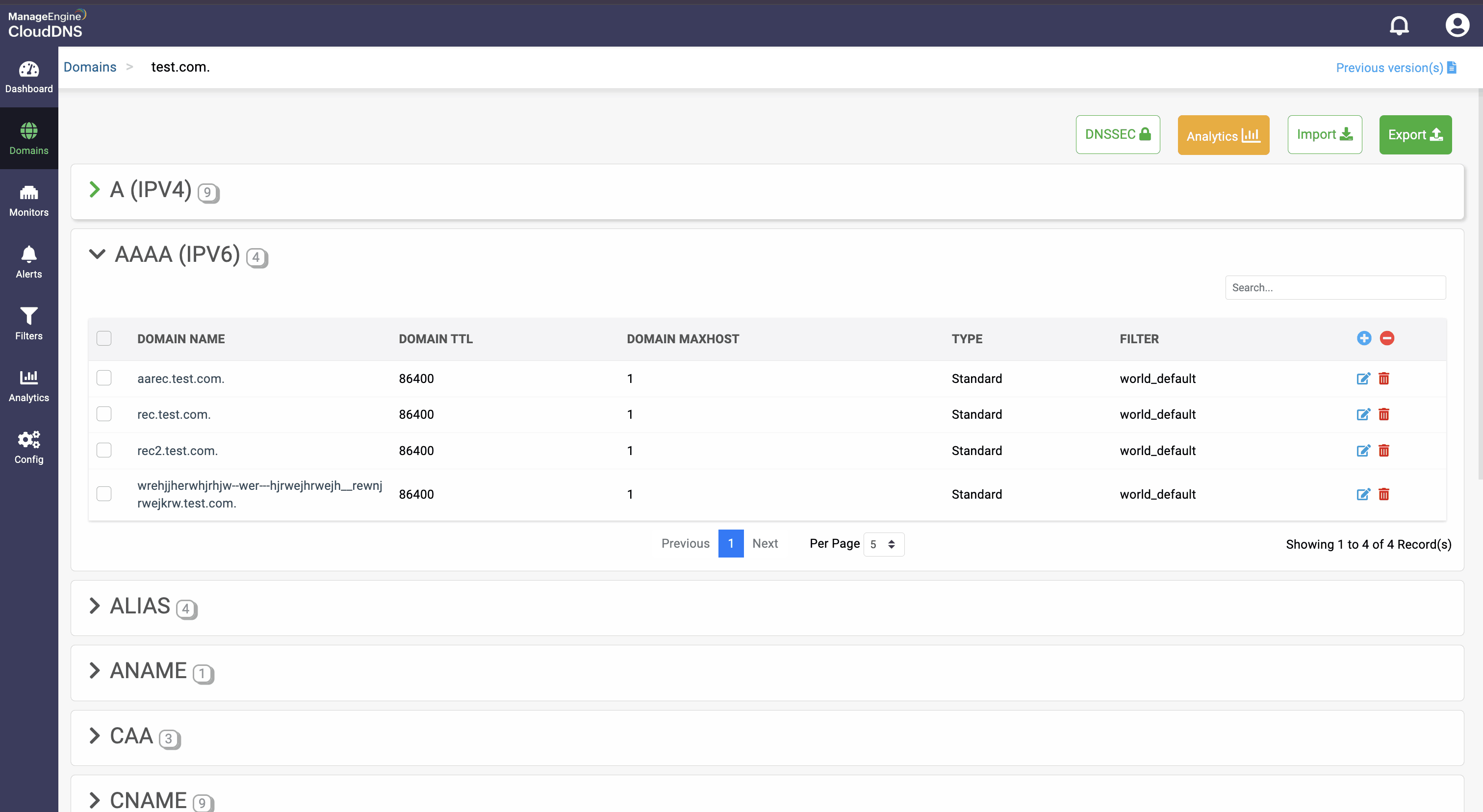
Step 3: Provide the details of the new AAAA record, such as name, TTL, date and time, and IP address.
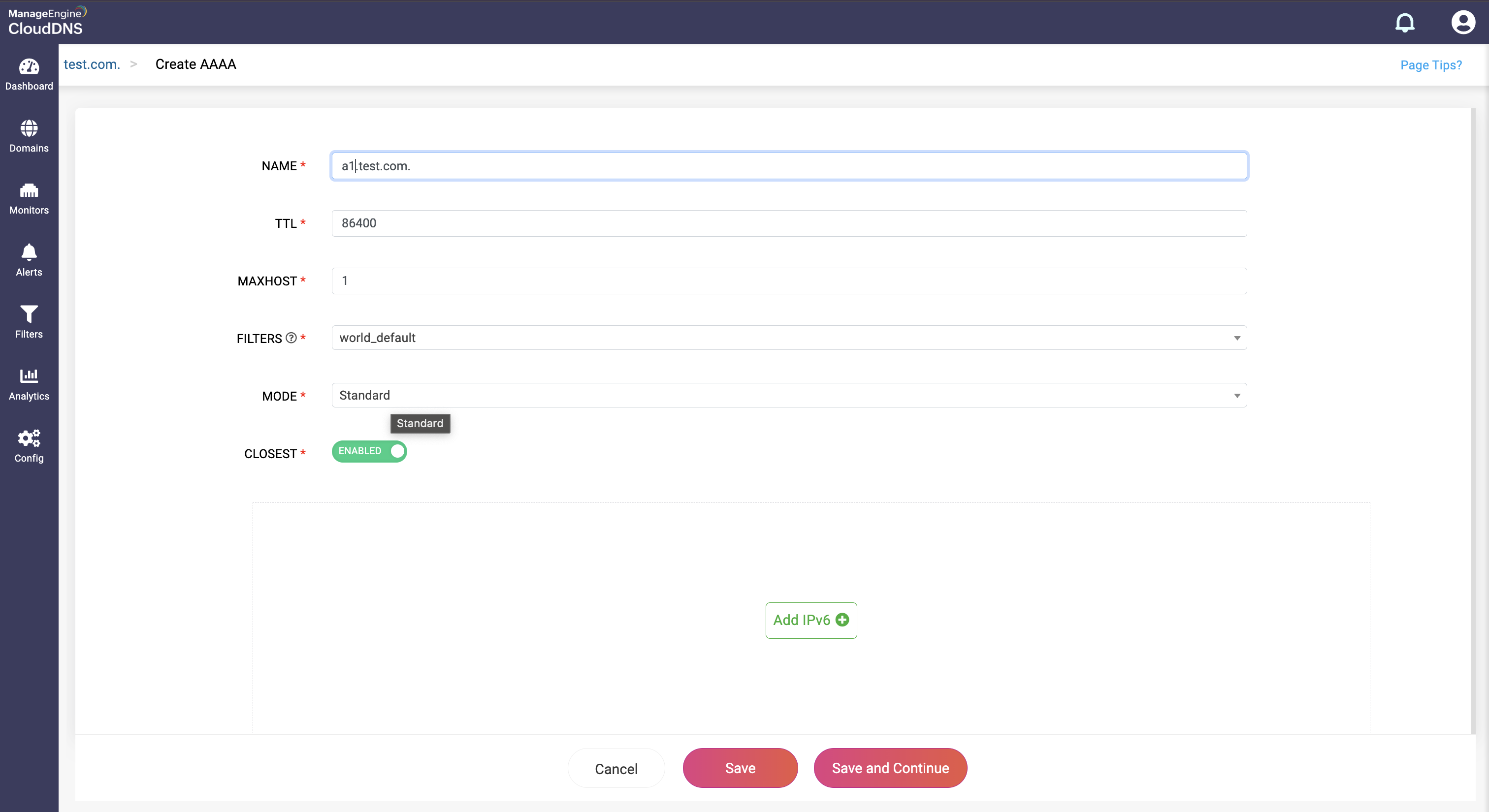
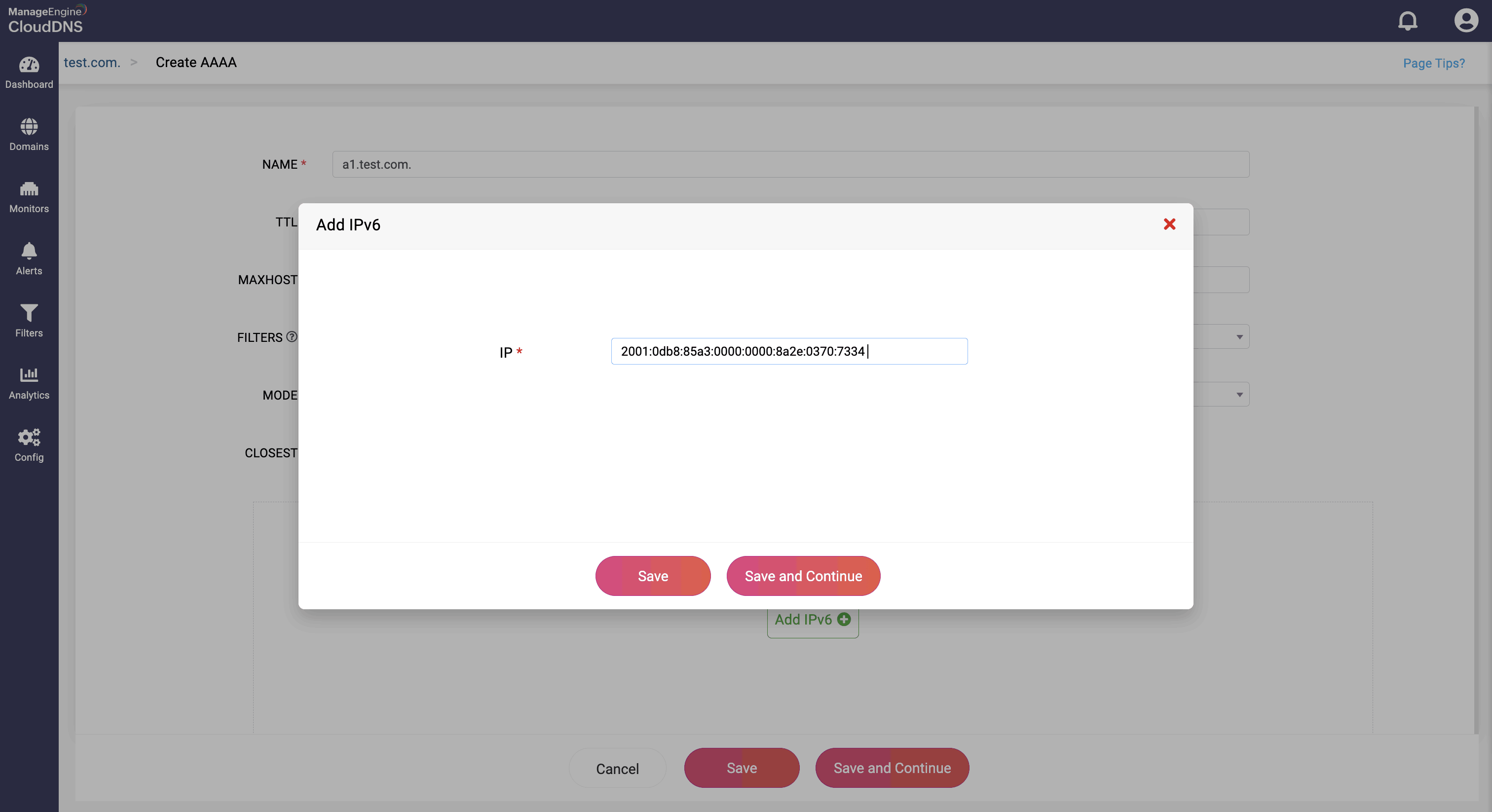
Step 4: Proceed to save the record by clicking on "Save" or "Save and Continue" to keep adding more entries to the record.
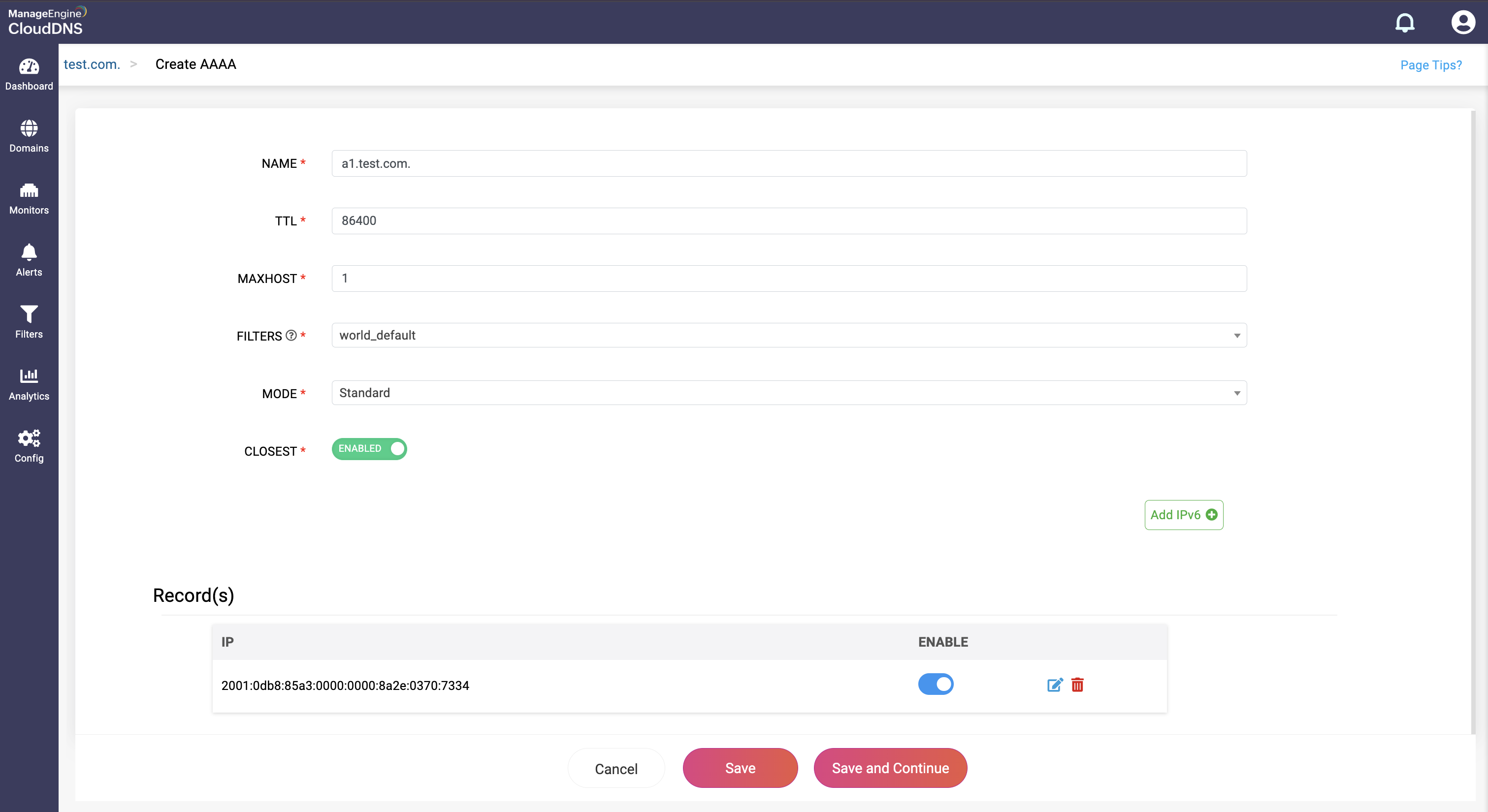
What is an ALIAS DNS record
An ALIAS record is a DNS record type that acts like a CNAME but can be used at the root domain (zone apex), which normal CNAMEs can't. It points your domain (like example.com) to another domain (like app.heroku.com) and automatically resolves it to A or AAAA records behind the scenes. It's useful for hosting platforms or CDNs that require domain-level pointing.
How do you create an ALIAS record?
Step 1: On the Domains page, click on a domain name of your choice to access its records. Navigate to the ALIAS record section
Step 2: On the right side, you can view a "+" sign for adding a record, and a "-" sign for deleting a record. Click the "+" sign to add a new ALIAS record.
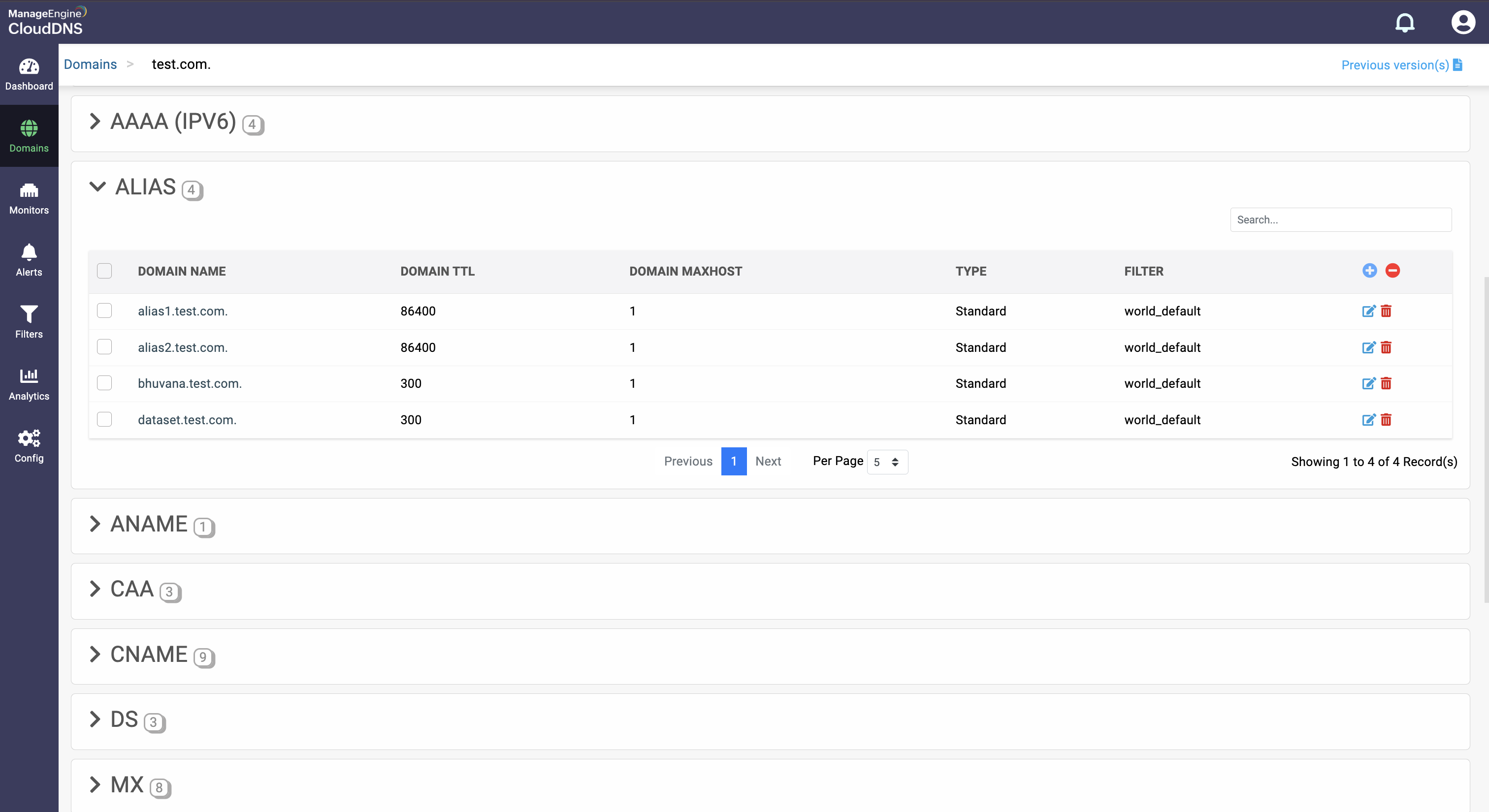
Step 3: Provide the details of the new ALIAS record, such as name, TTL, date and time, and host.
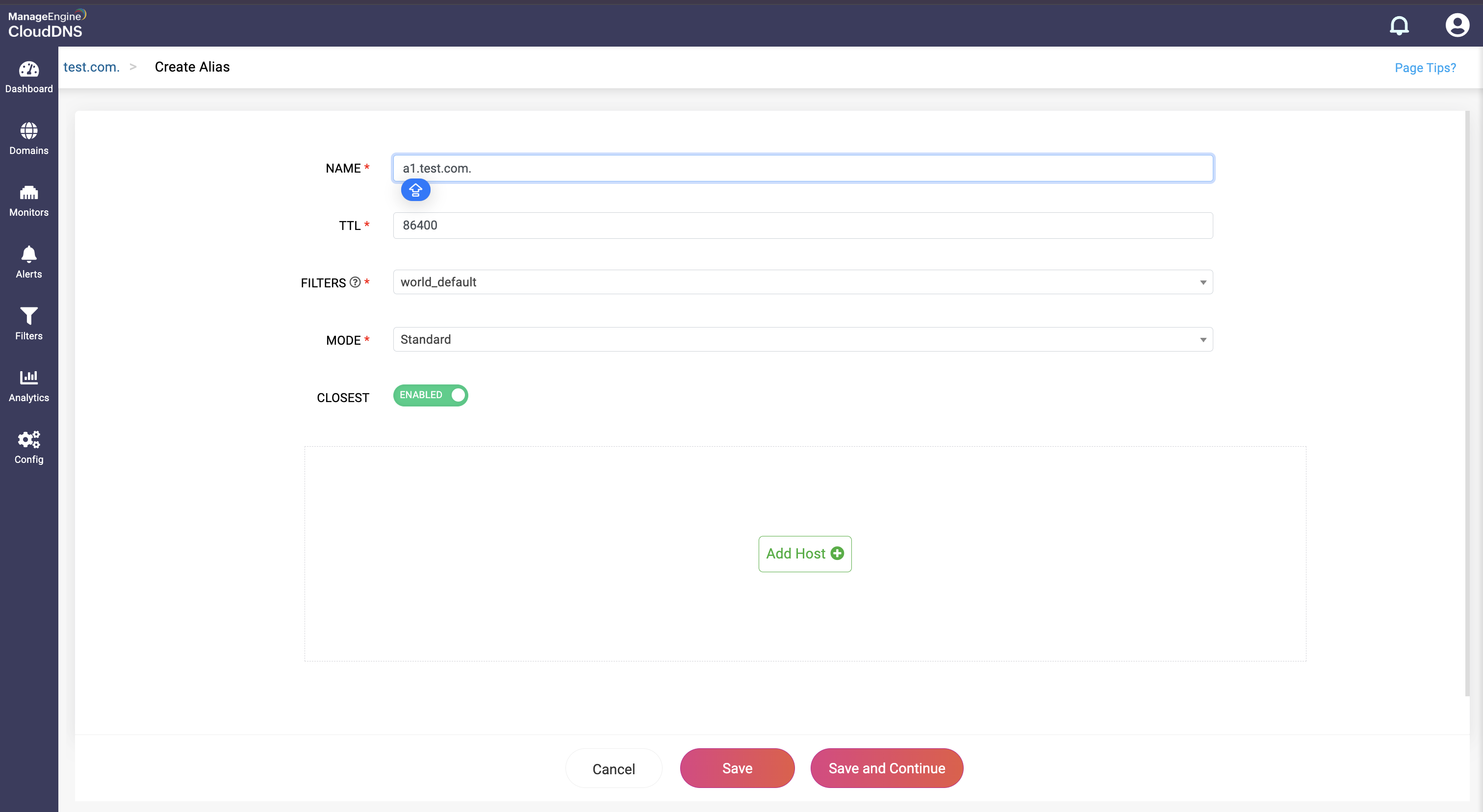
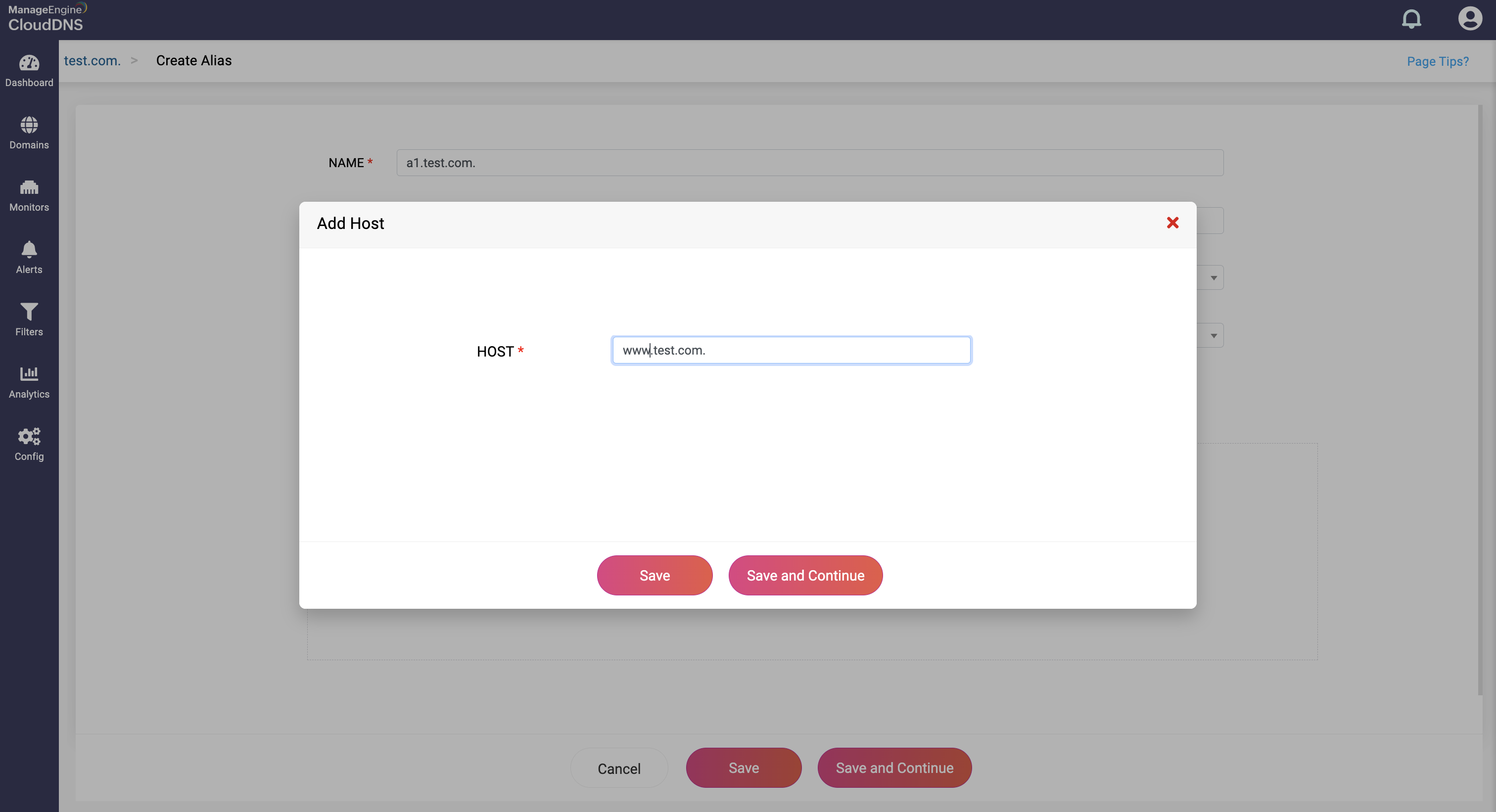
Step 4: Proceed to save the record by clicking on "Save" or "Save and Continue" to keep adding more entries to the record.
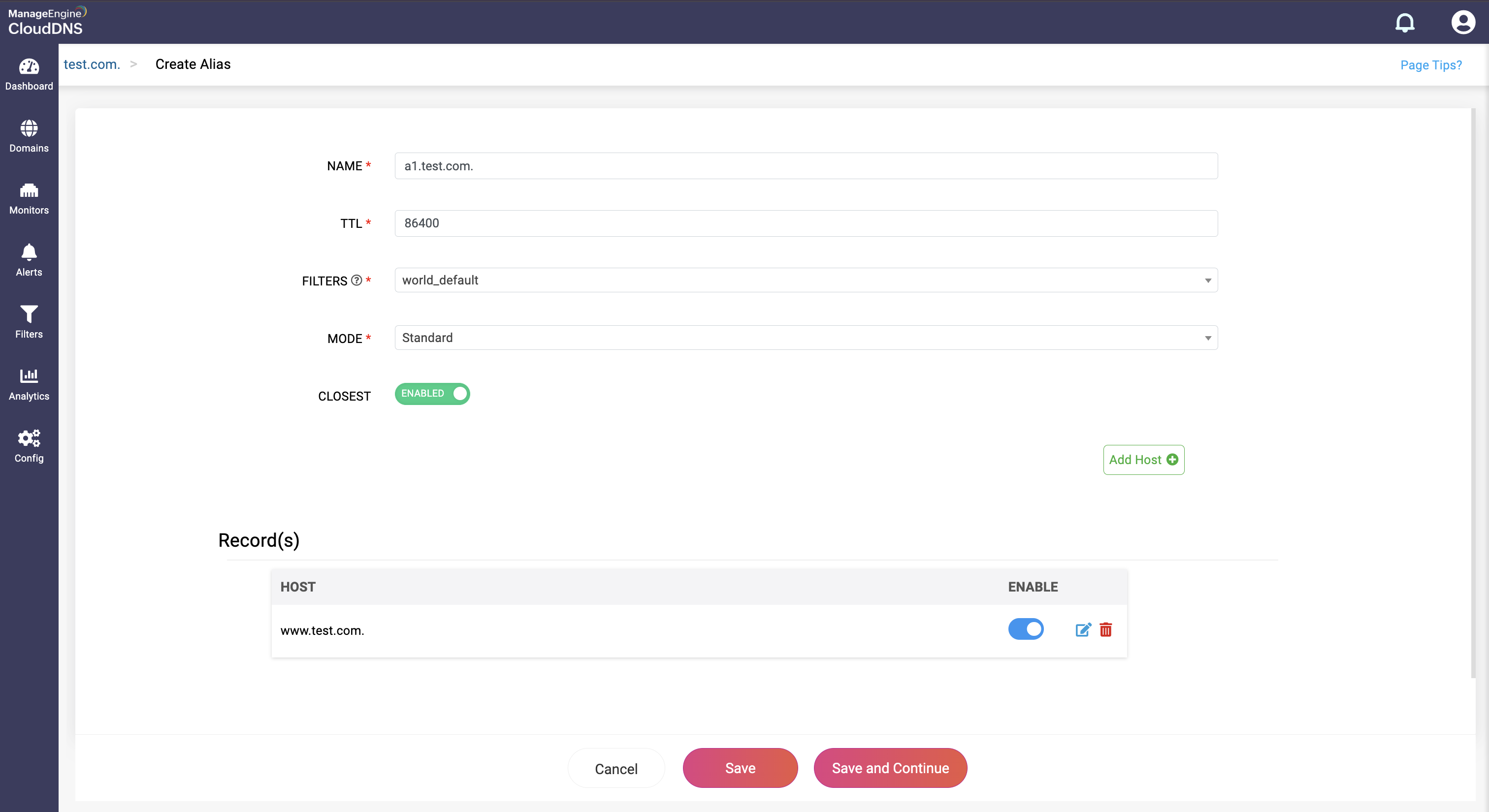
What is an ANAME DNS record
How do you create an ANAME record?
Step 1: On the Domains page, click on a domain name of your choice to access its records. Navigate to the ANAME record section
Step 2: On the right side, you can view a "+" sign for adding a record, and a "-" sign for deleting a record. Click the "+" sign to add a new ANAME record.
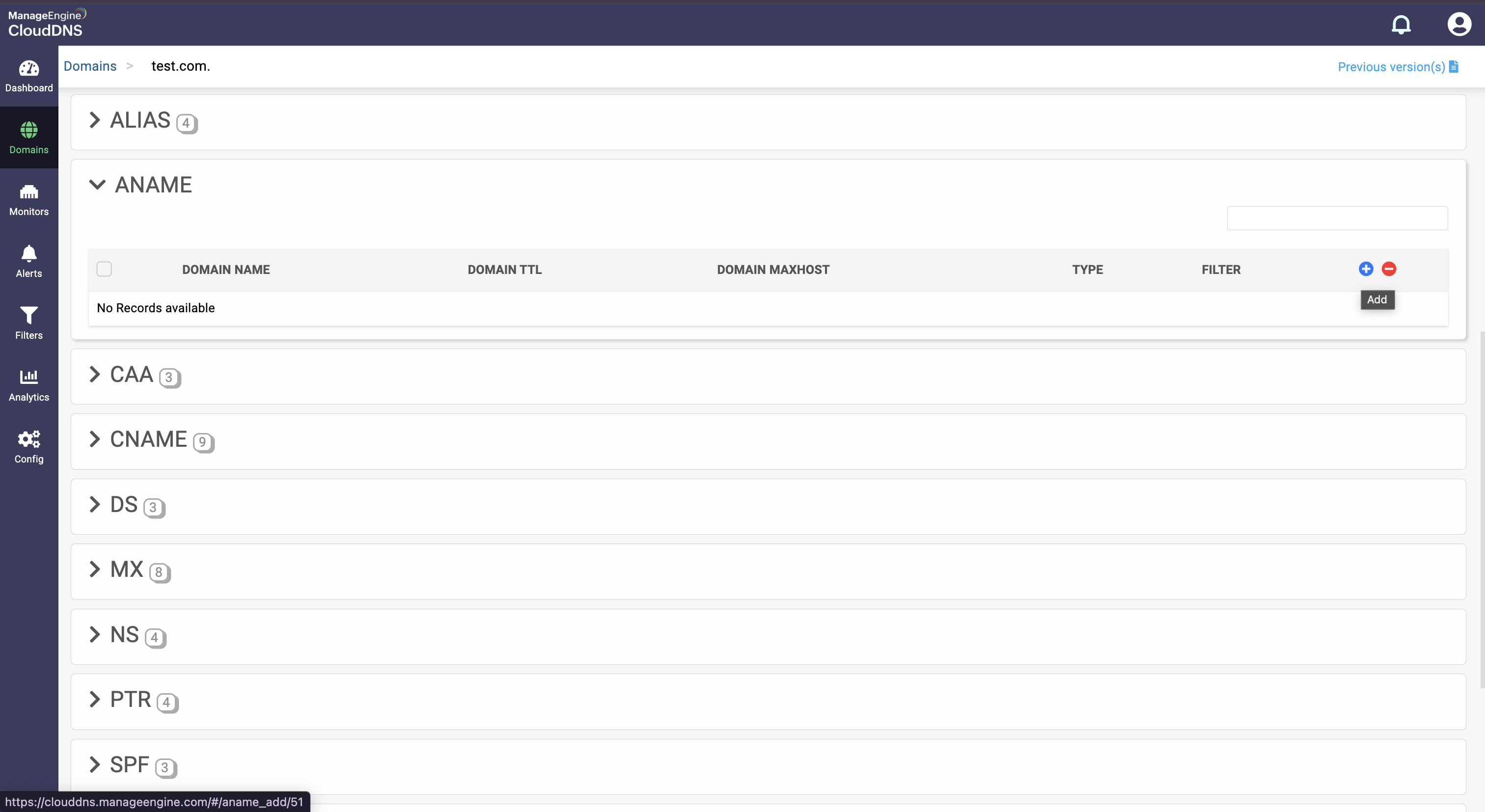
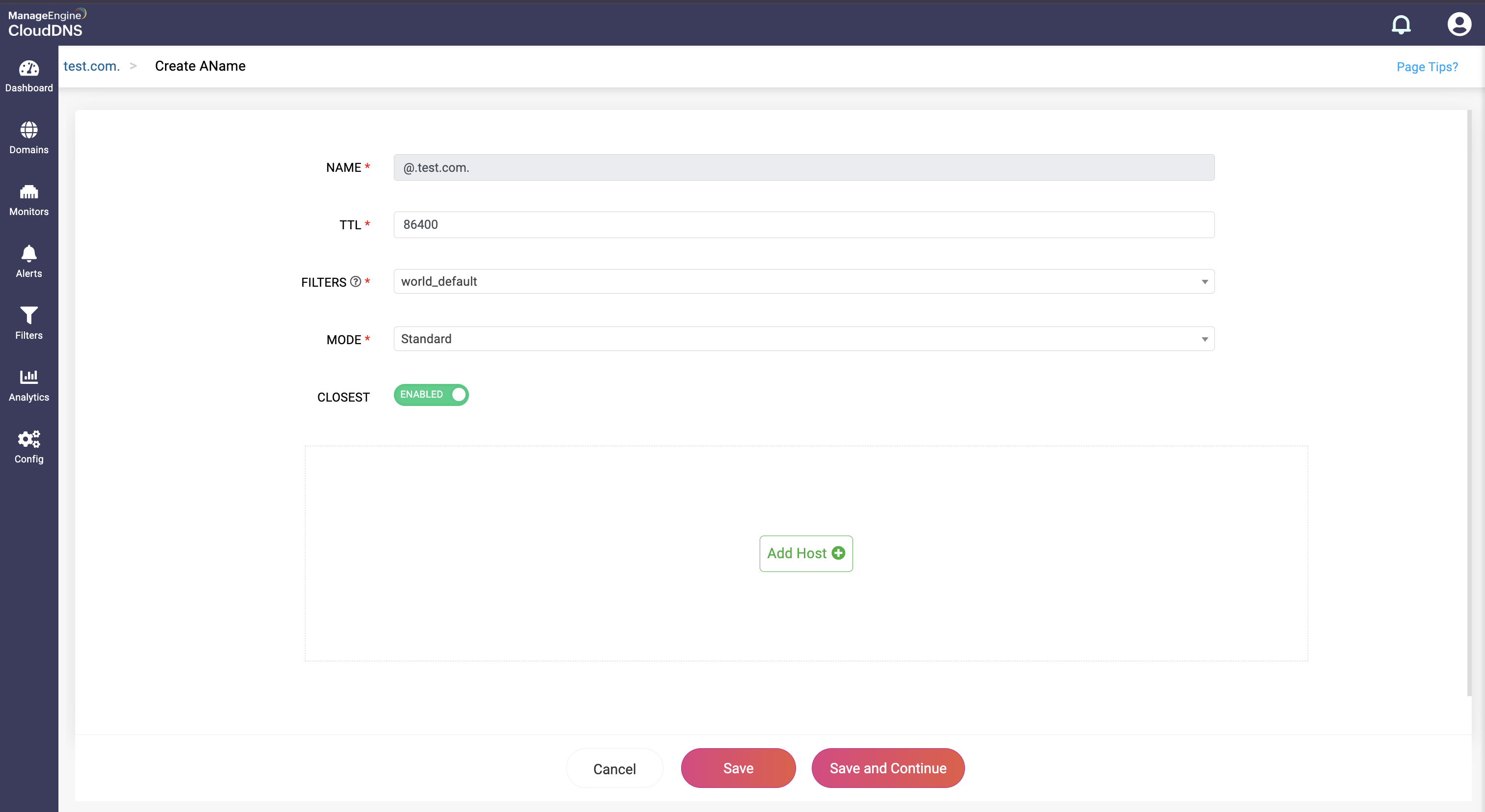
Step 3: Provide the details of the new ANAME record, such as name, TTL, date and time, and host.
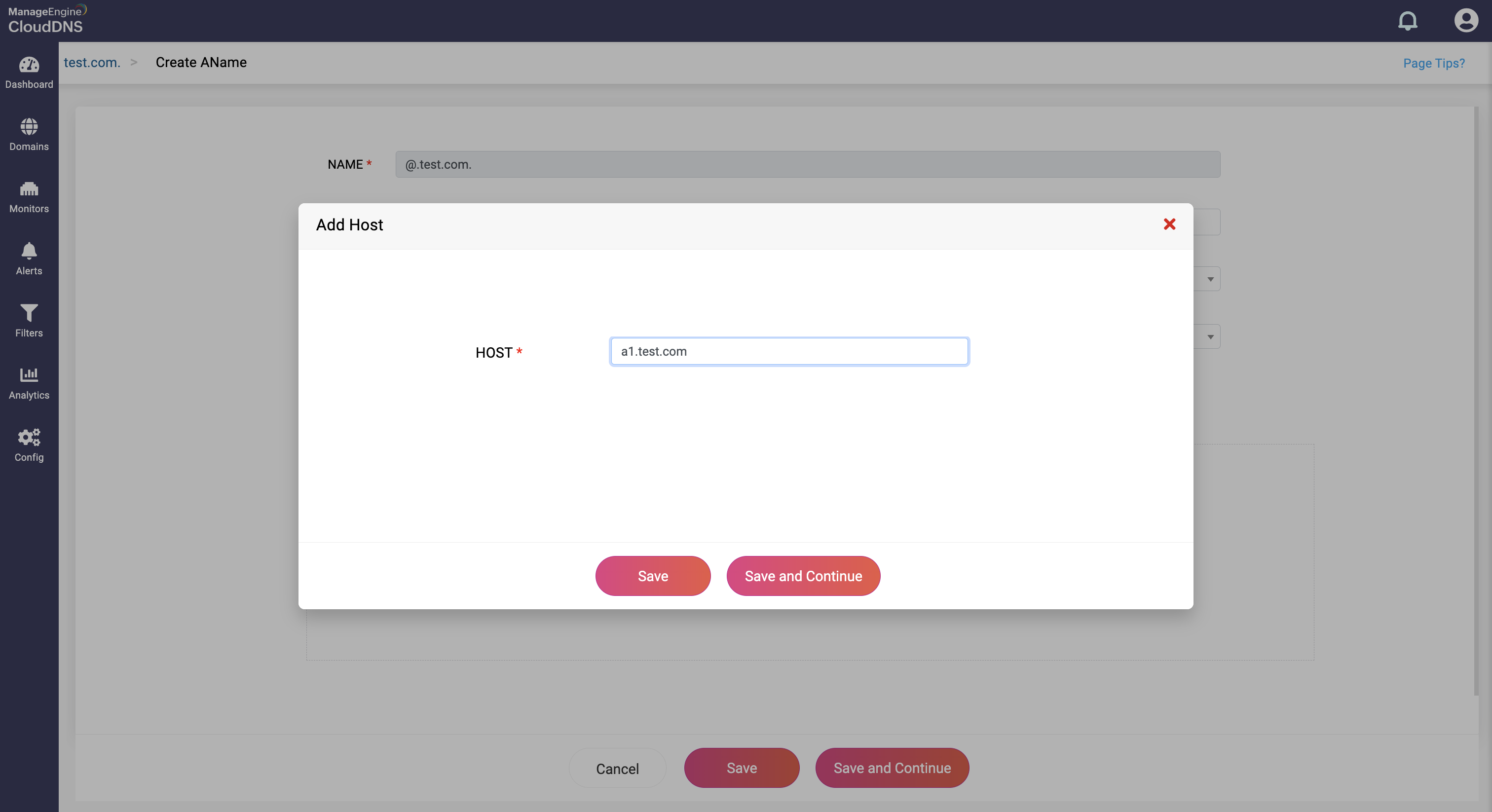
Step 4: Proceed to save the record by clicking on "Save" or "Save and Continue" to keep adding more entries to the record.
What is a CAA record
Certificate Authority Authorization (CAA) record details about which certificate authorities (CAs) are valid so they can issue certificates for a domain name. This ensures that only trusted CAs are issuing SSL and TLS certificates for authorized domains, while preventing unauthorized CAs from issuing certificate for malicious domains.
CAA records acts a permit entry for identifying and allowing trustable CAs for reliable certificate issuance.
How do you create a CAA record?
Step 1:On the Domains page, click on a domain name of your choice to access its records. Navigate to the CAA record section.
Step 2: On the right side, you can view a "+" sign for adding a record, and a "-" sign for deleting a record. Click the "+" sign to add a new CAA record.
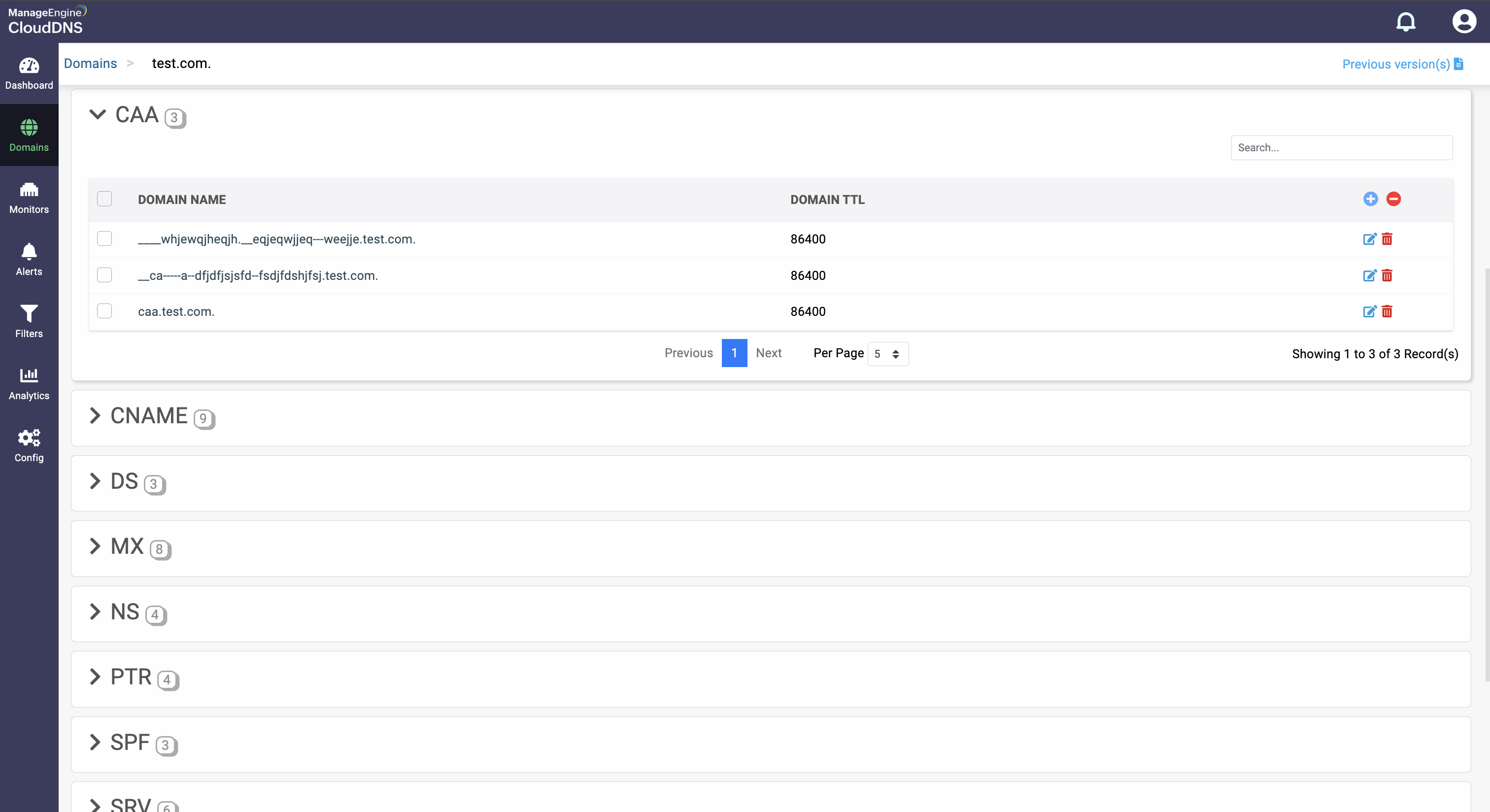
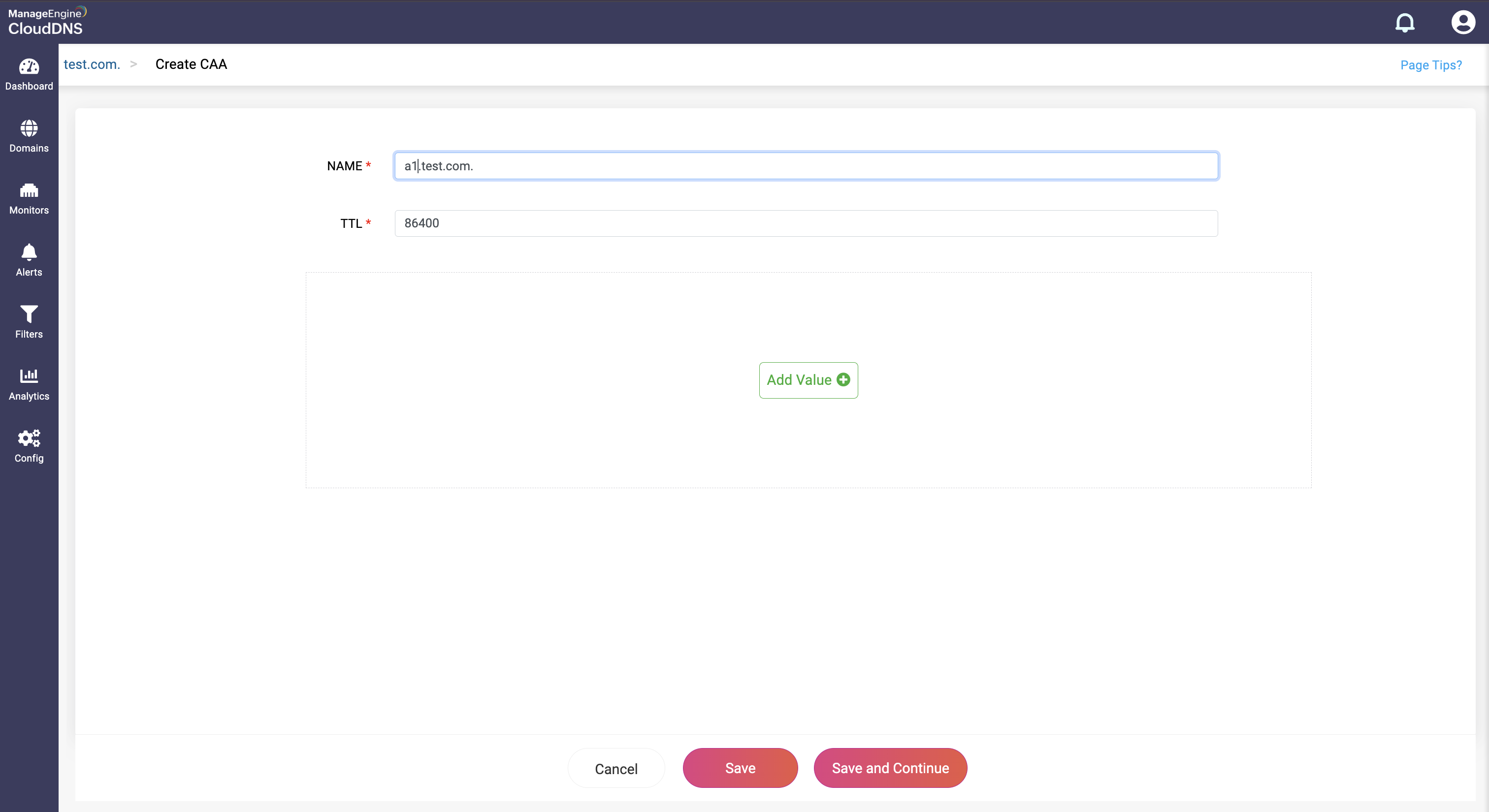
Step 3: Provide the details of the new CAA record, such as name, TTL, date and time, there are three values in the Add Value section.
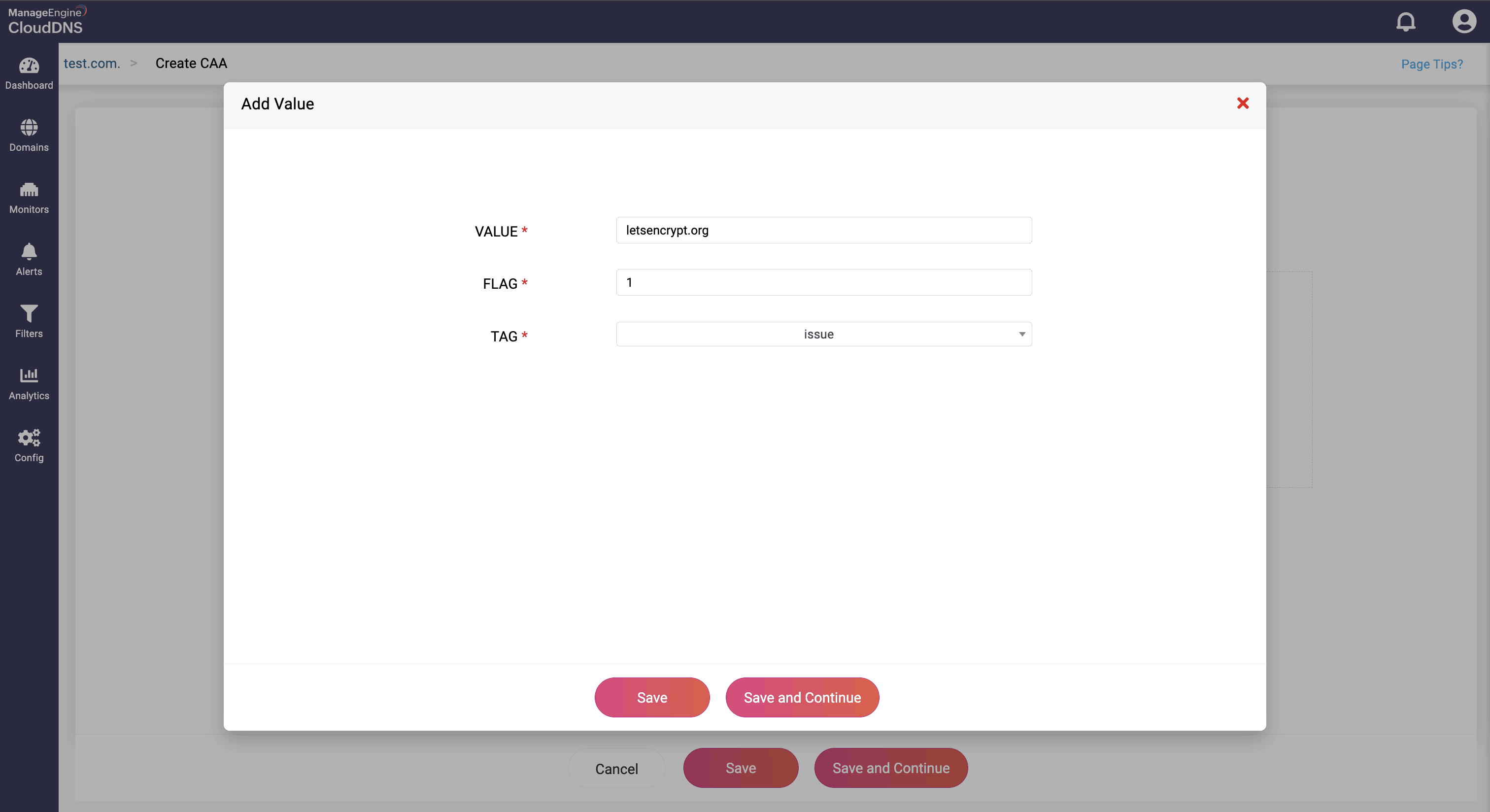
Value: This field specifies the domain name of the certificate authority allowed to issue certificates for the zone.
Flag: This field specifies properties or directives associated with the record. Common flag values:
- 0: No specific flag; standard behavior.
- 128: Indicates the record is critical, meaning it must be understood and processed by the CA.
The tag identifies the purpose of the CAA record. Common tags include:
- issue: Authorizes a specific CA to issue certificates for the domain.
- issuewild: Authorizes a CA to issue wildcard certificates for the domain.
- iodef: Specifies a URL or email to report invalid certificate requests.
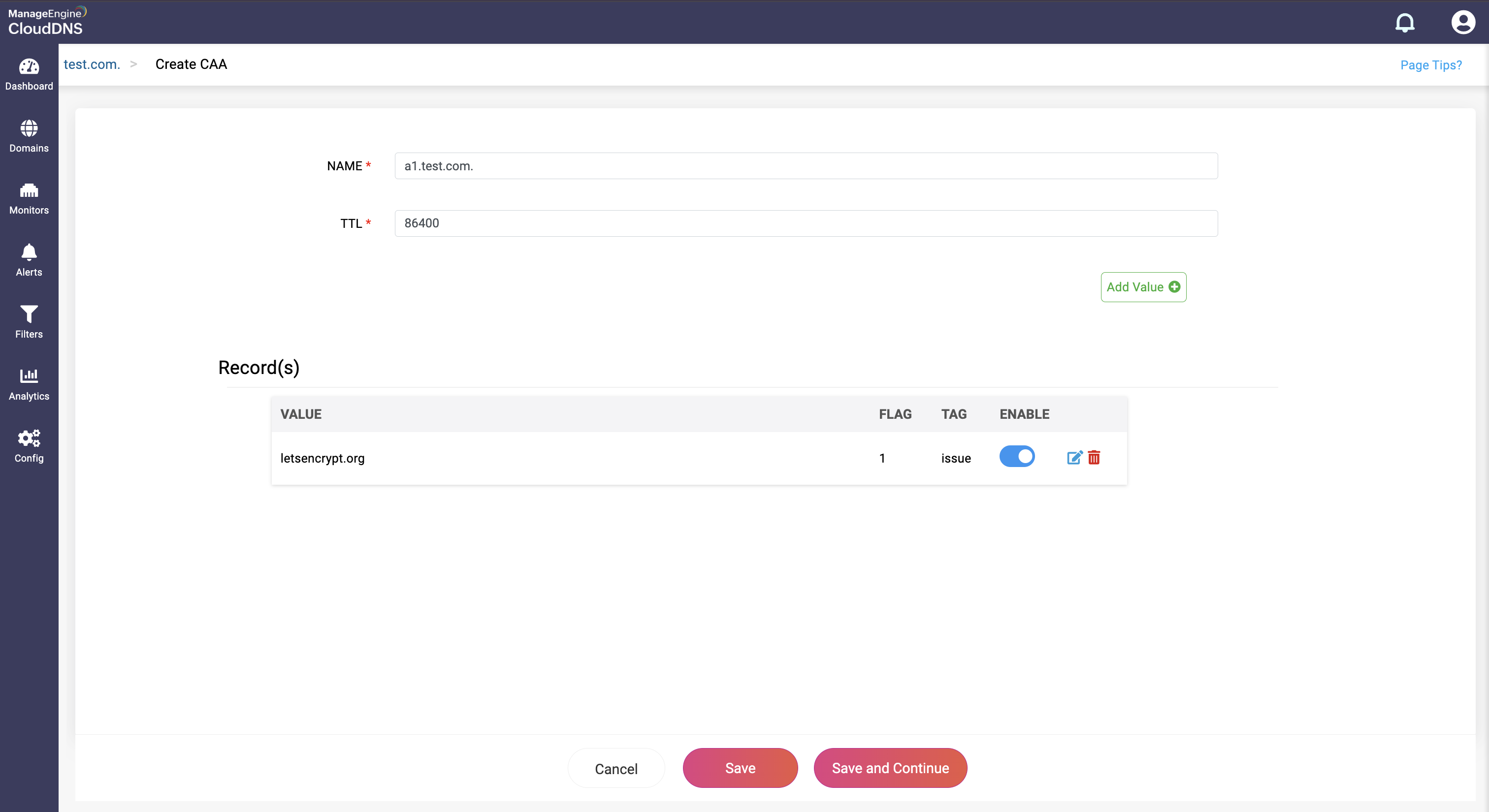
Step 4: Proceed to save the record by clicking on "Save" or "Save and Continue" to keep adding more entries to the record.
What is a CNAME record
CNAME records help map an alias domain name to a canonical domain name. Alias domain names assist users with finding the true/canonical domain name. CNAME records helps by associating multiple alias domain names to a single canonical domain name.
CNAME records are primarily used to simplify DNS management, enhance server load balancing and failover.
How do you create a CNAME record?
Step 1:On the Domains page, click on a domain name of your choice to access its records. Navigate to the CNAME record section.
Step 2: On the right side, you can view a "+" sign for adding a record, and a "-" sign for deleting a record. Click the "+" sign to add a new CNAME record.
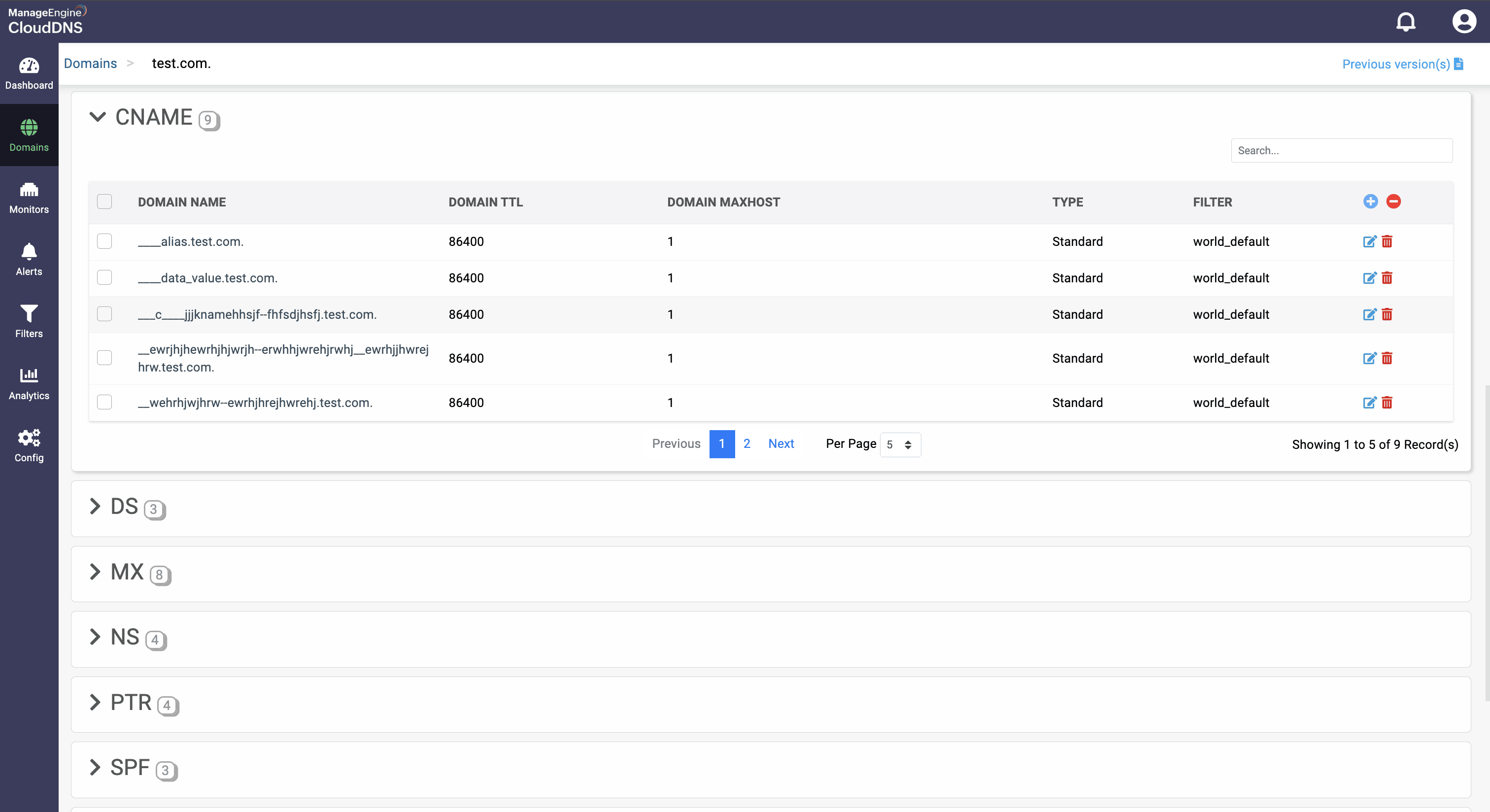
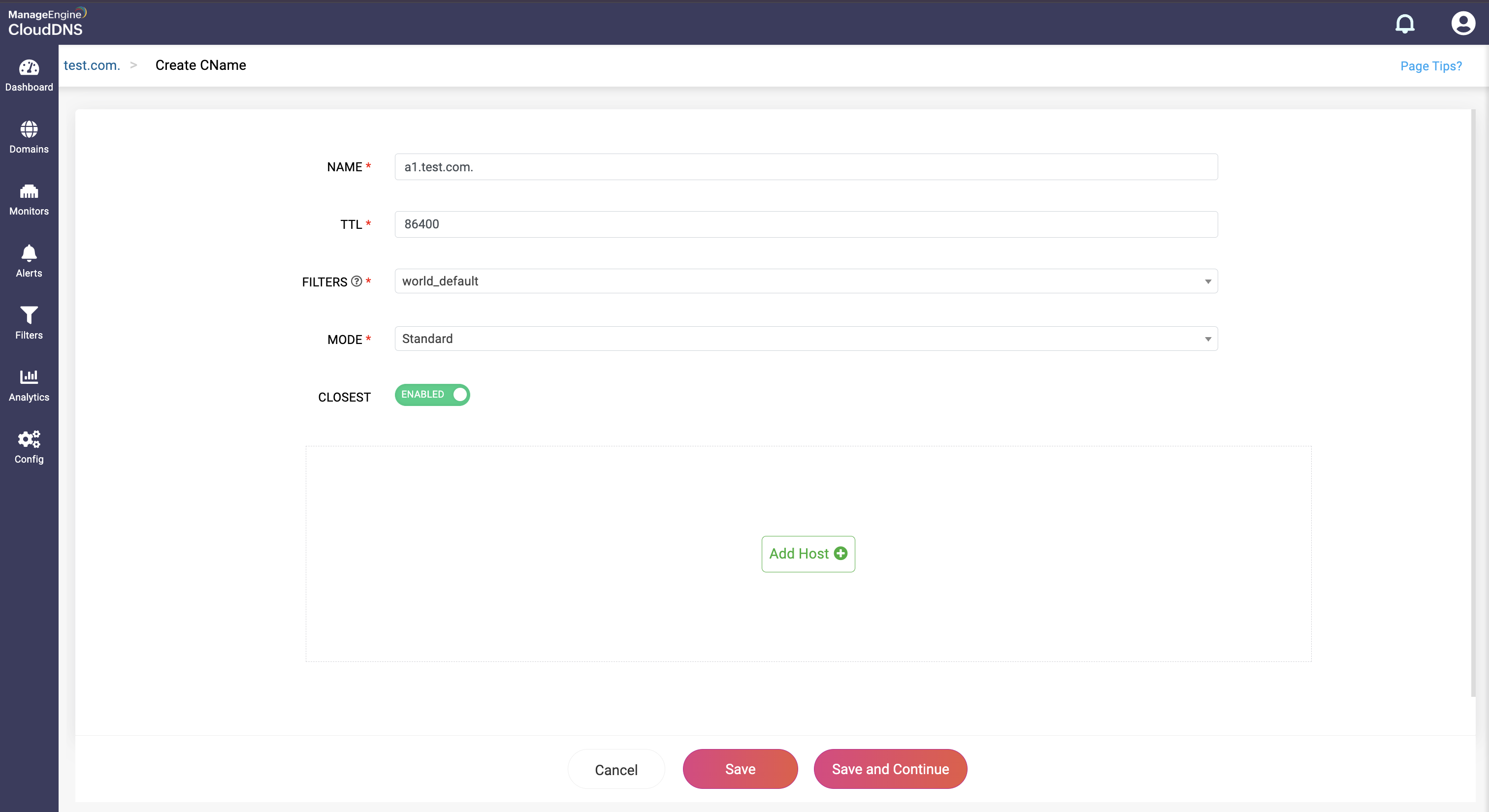
Step 3: Provide the details of the new CNAME record, such as name, TTL, date and time.
Provide the alias domain that points to the canonical domain in the Host field.
Note:A CNAME record can only point to one canonical (target) domain. It cannot have multiple targets directly. To represent multiple aliases pointing to different canonical domains, you must create separate CNAME records for each alias.
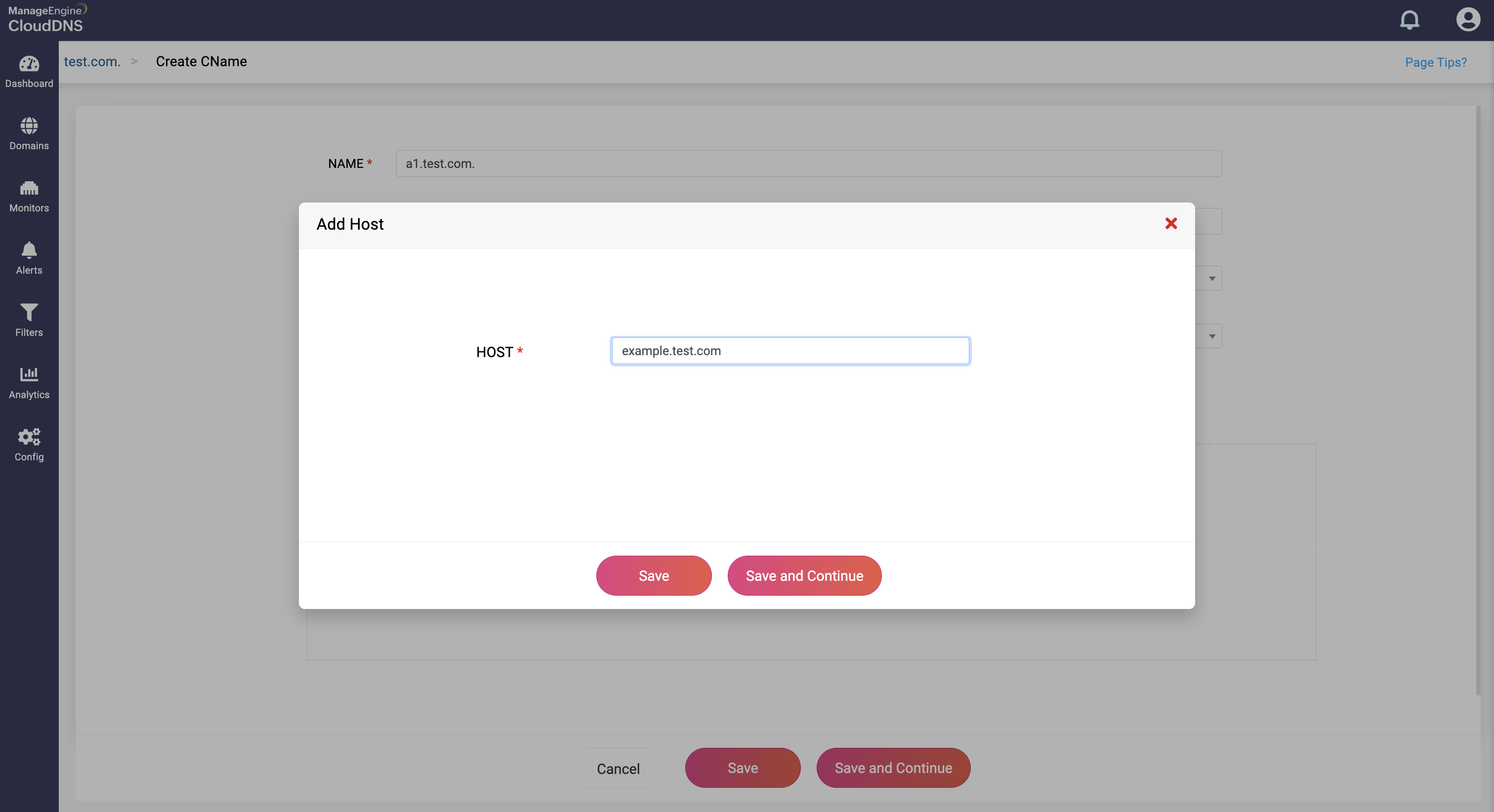
Step 4: Proceed to save the record by clicking on "Save" or "Save and Continue to keep adding more entries to the record.
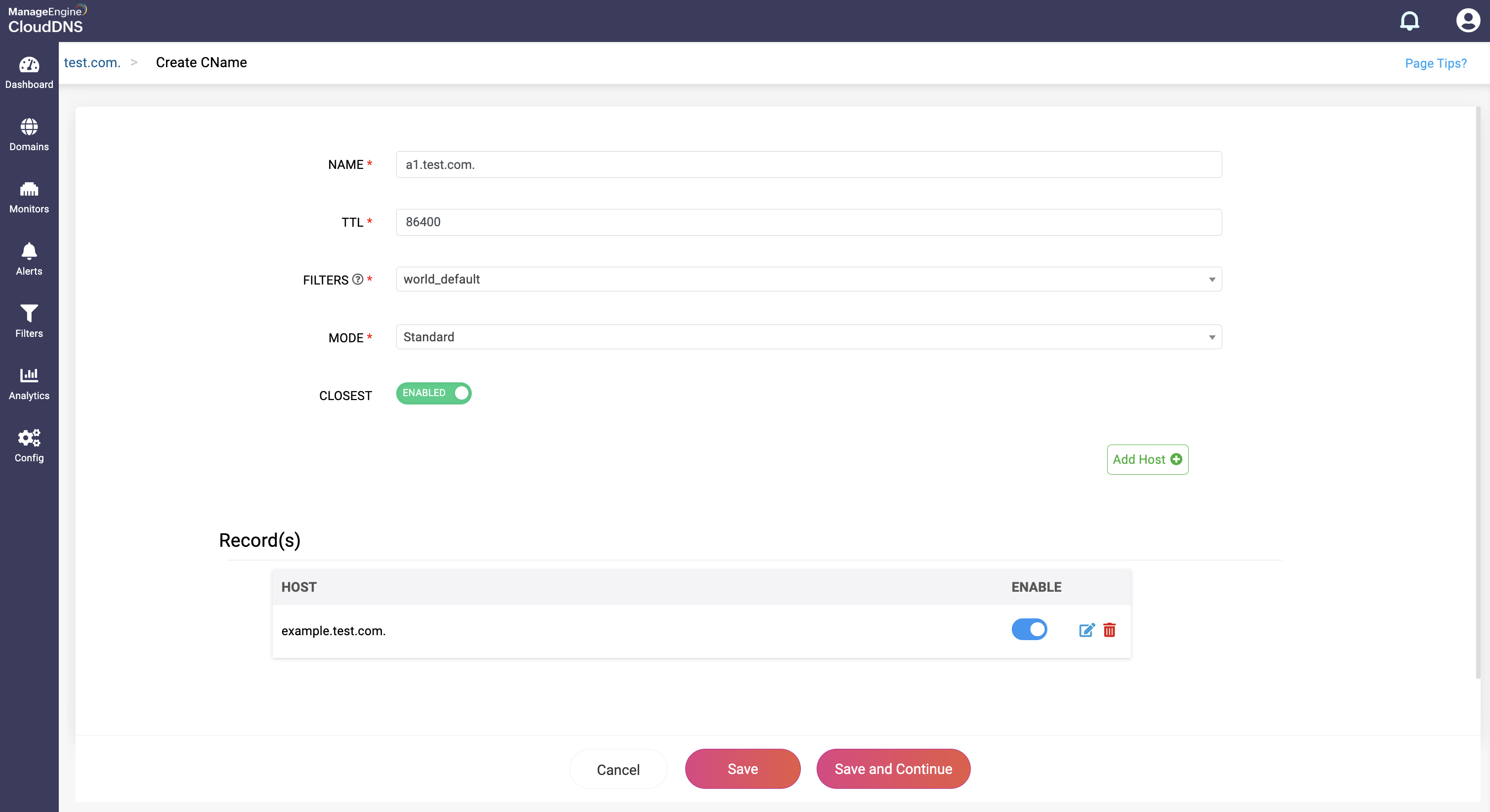
What is a DS record
Delegate Signature (DS) records are used in the Domain Name System Security Extensions (DNSSEC) for digital signing for DNS information transferred from the server to the client. This helps secure the integrity and authenticity of the DNS response and creates a chain of trust by digitally signing each server.
DS records prevents DNS spoofing and cache poisoning by securing the DNS response.
How do you create a DS record?
Step 1:On the Domains page, click on a domain name of your choice to access its records. Navigate to the DS record section.
Step 2: On the right side, you can view a "+" sign for adding a record, and a "-" sign for deleting a record. Click the "+" sign to add a new DS record.
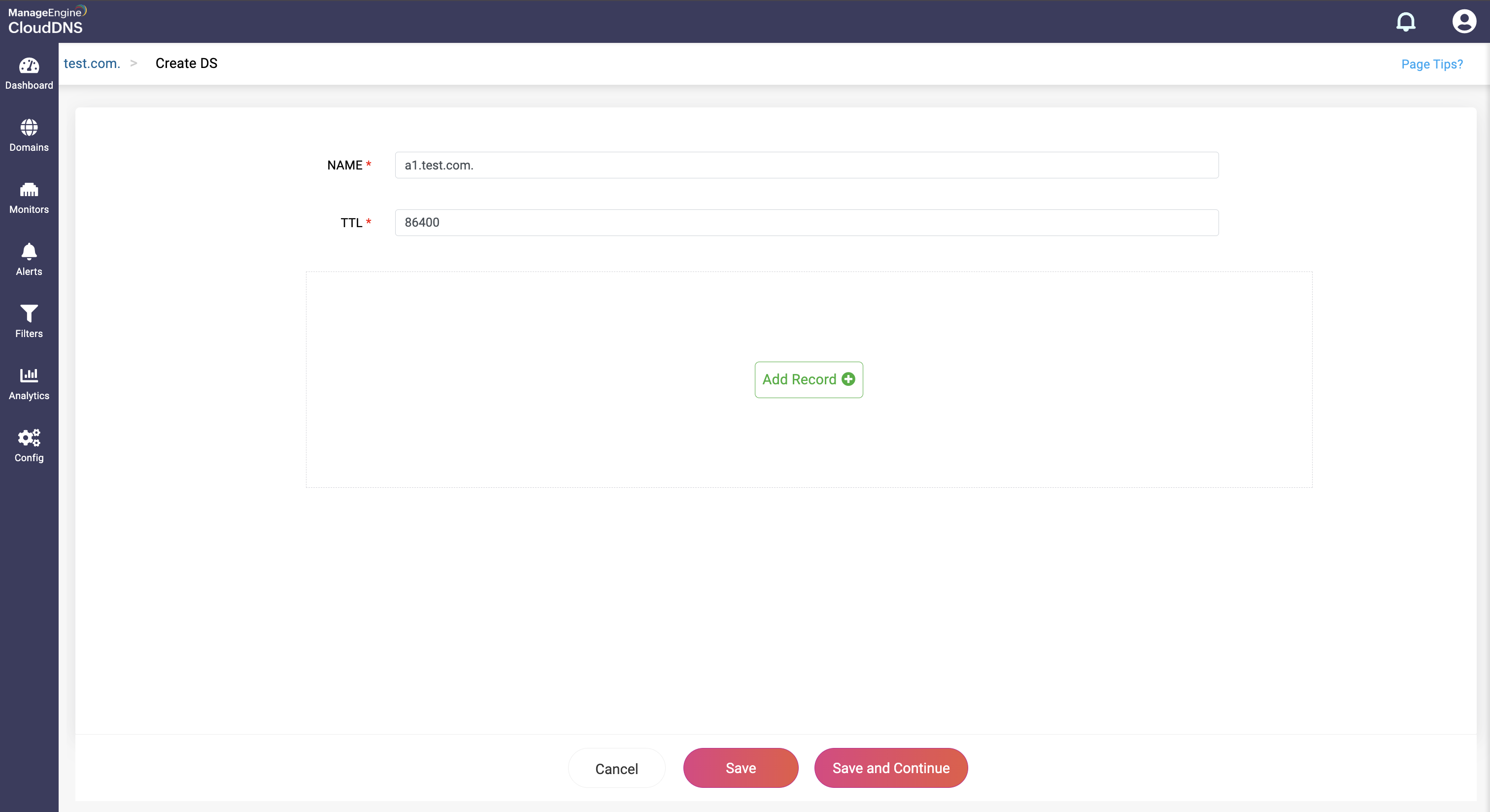
Step 3: Provide the details of the new DS record, such as name, TTL, date and time. There are four fields in the Add Record section.
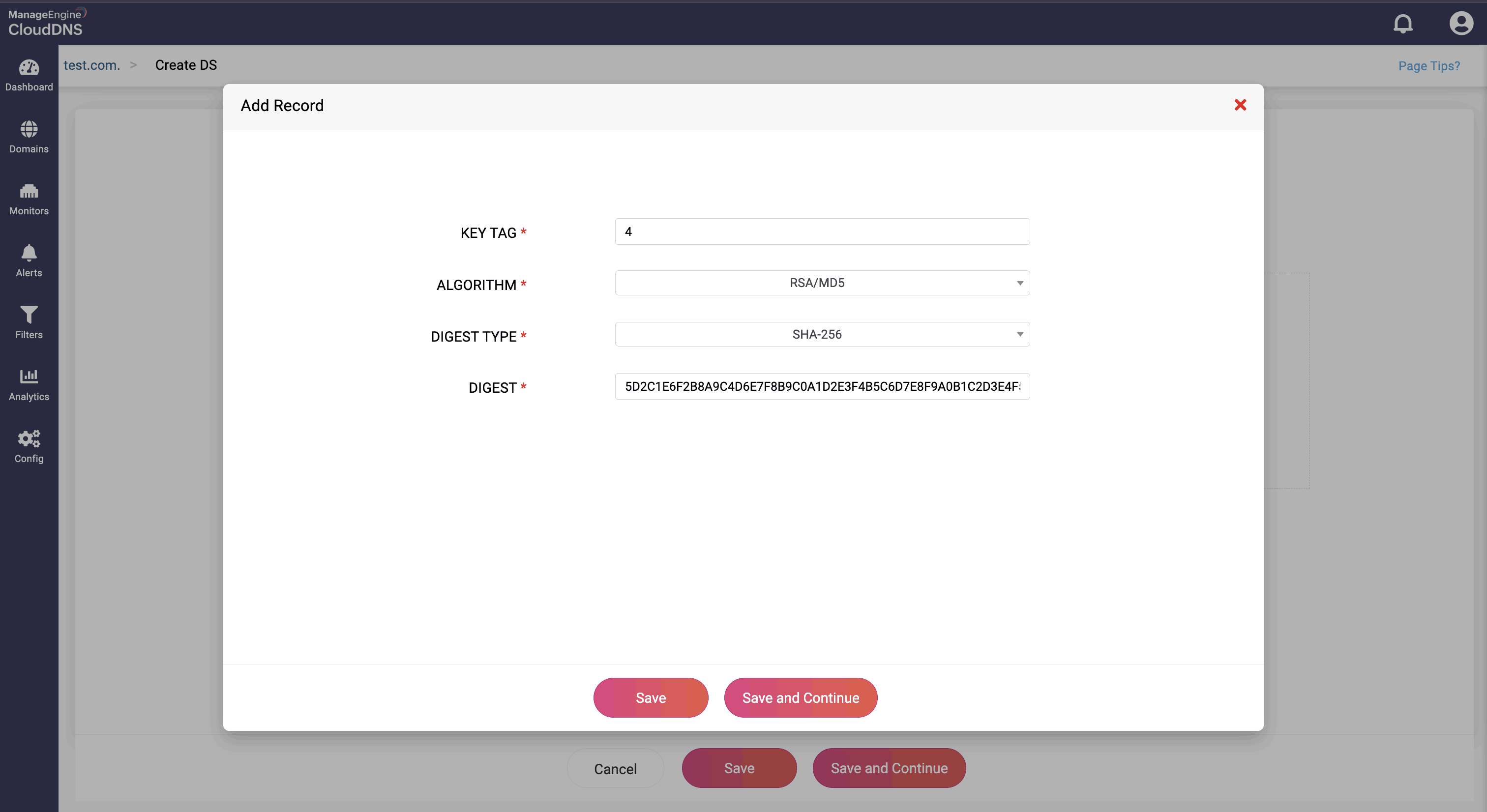
- Key Tag: This field contains a short numeric identifier for the DNSKEY record to which the DS record is pointed
- Algorithm: This field specifies the algorithm used by the DNSKEY record and each algorithm is assigned a number. The common algorithms are: 1: RSA/MD5 5: RSA/SHA-1 8: RSA/SHA-256 13: ECDSA Curve P-256 with SHA-256
- Digest type: This field specifies the algorithm used to create the digest (hash) of the DNSKEY record. Each digest type is assigned a number. Common digest types include: 1: SHA-1 2: SHA-256 4: SHA-384
- Digest: This field contains the actual cryptographic hash of the DNSKEY record. It ensures that the DNSKEY record has not been tampered with.
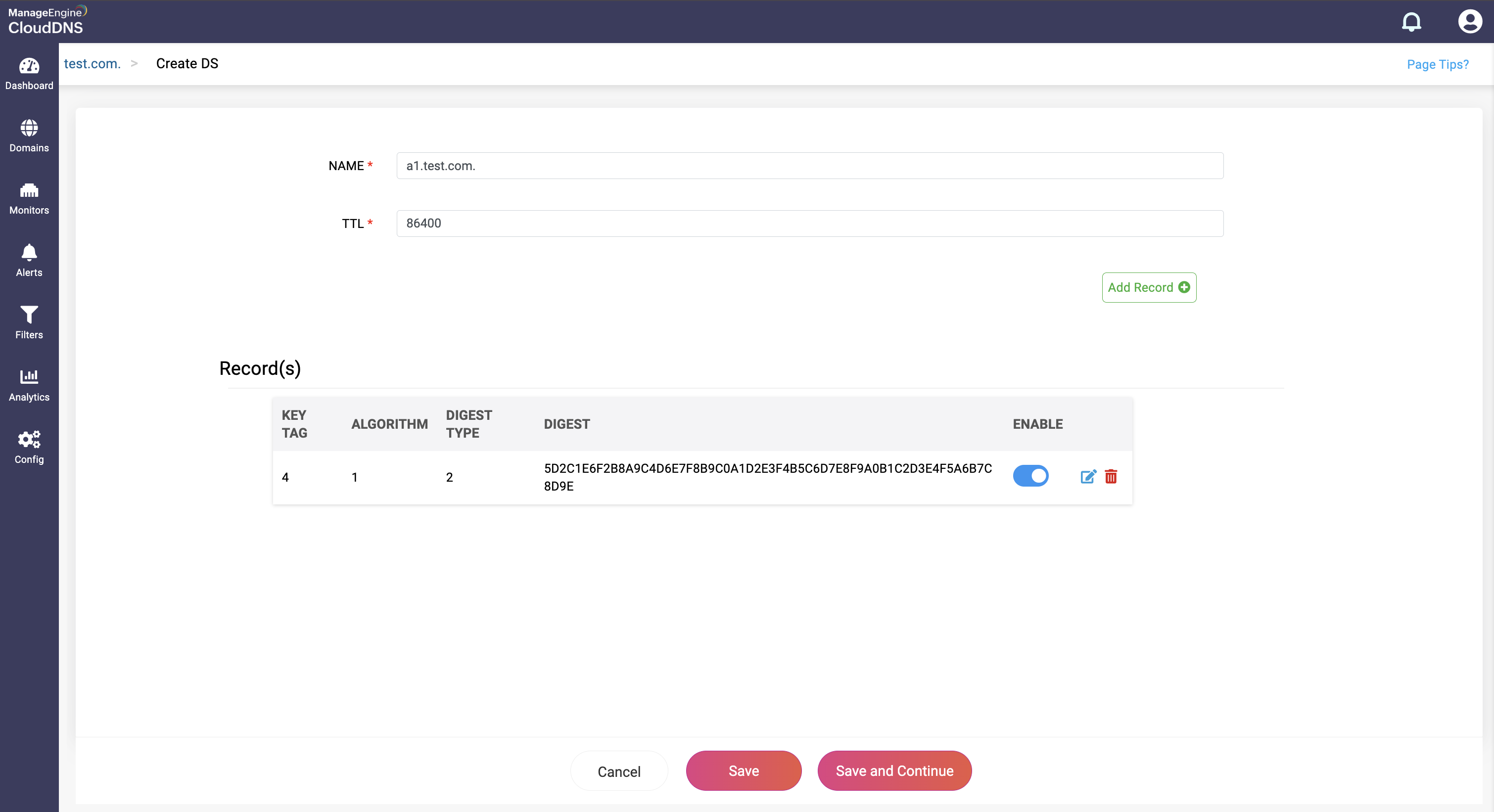
Step 4: Proceed to save the record by clicking on "Save" or "Save and Continue" to keep adding more entries to the record.
What is a MX record
MX records are primarily used in the mail servers for routing specific mail servers to handle mails of a specific domain and directing mail to the right mail servers.
When mail is sent to an address of a domain, the mail server will query the nearby DNS resolver for MX record of the recipient's domain. The MX record will provide the address of the recipient's mail server, and the mail will be directed.
How do you create a MX record?
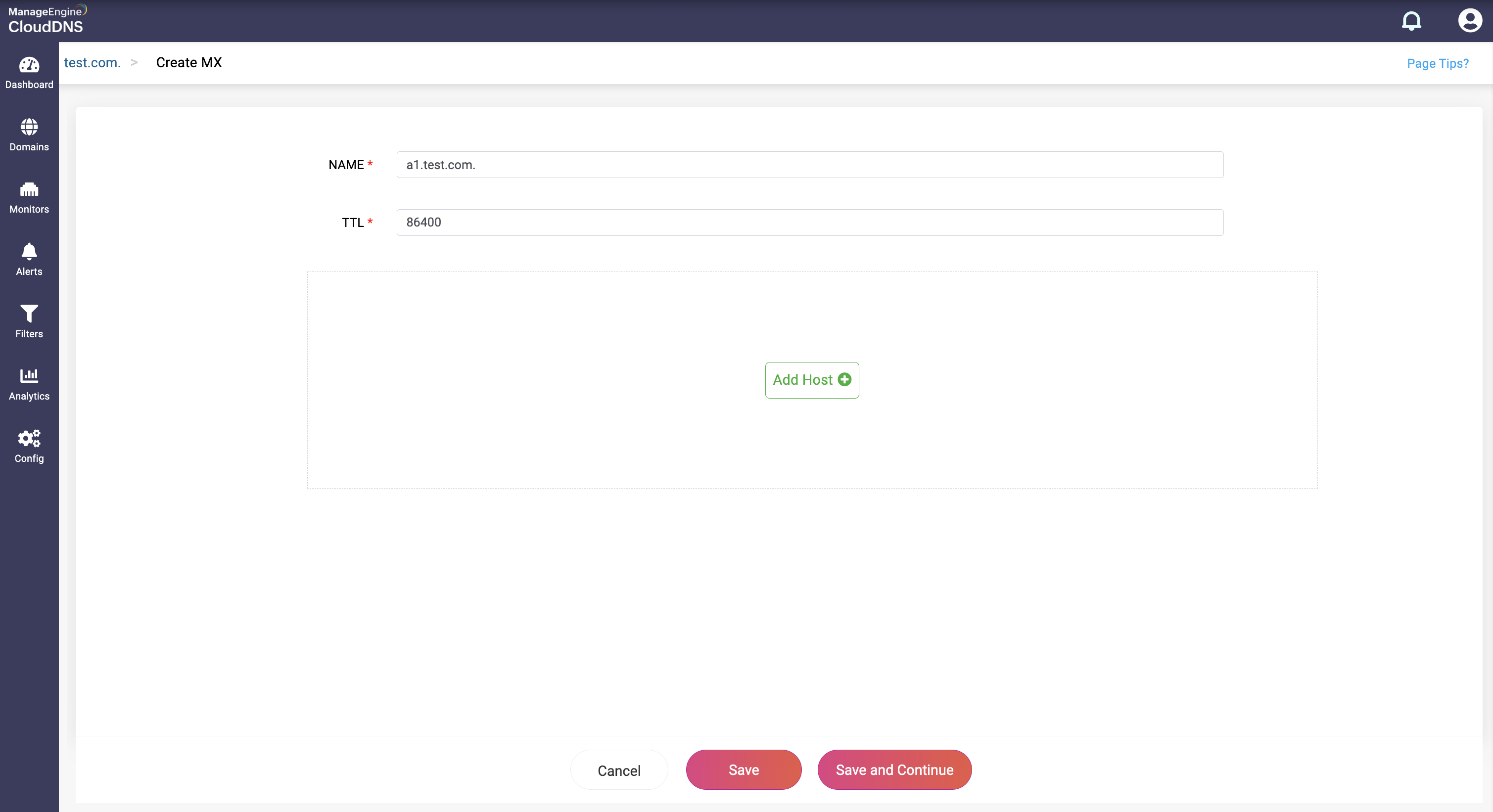
Step 1:On the Domains page, click on a domain name of your choice to access its records. Navigate to the MX record section.
Step 2: On the right side, you can view a "+" sign for adding a record, and a "-" sign for deleting a record. Click the "+" sign to add a new MX record.
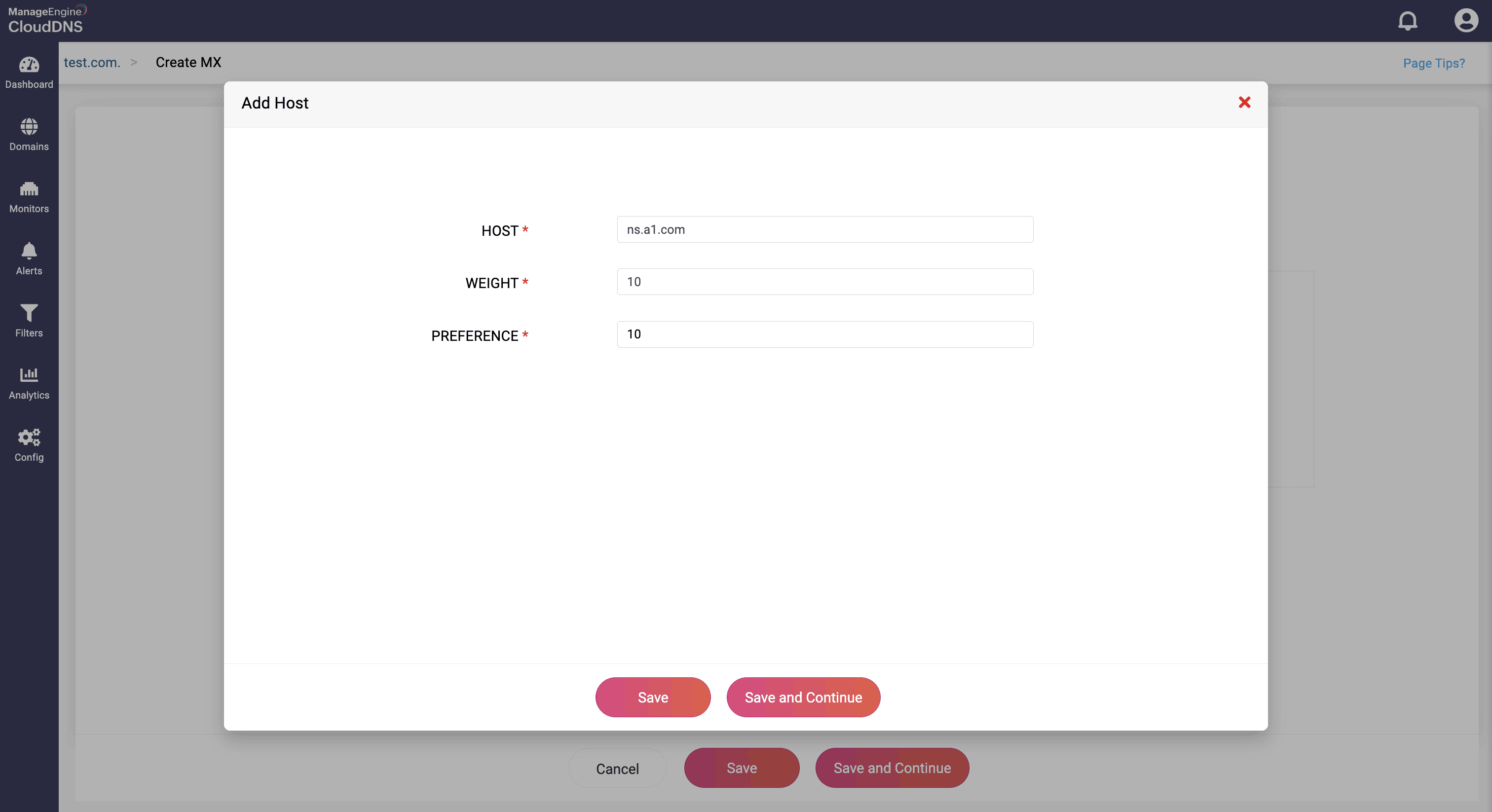
Step 3: Provide the details of the new MX record, such as name, TTL, date and time. There are two fields in the Add Host section.
Host: This field contains the Full Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) of the mail server.
Preference: This field is an integer value that indicates the priority of the mail server. Lower values have higher priority. If multiple MX records exist for a domain, the mail server with the lowest preference value is tried first.
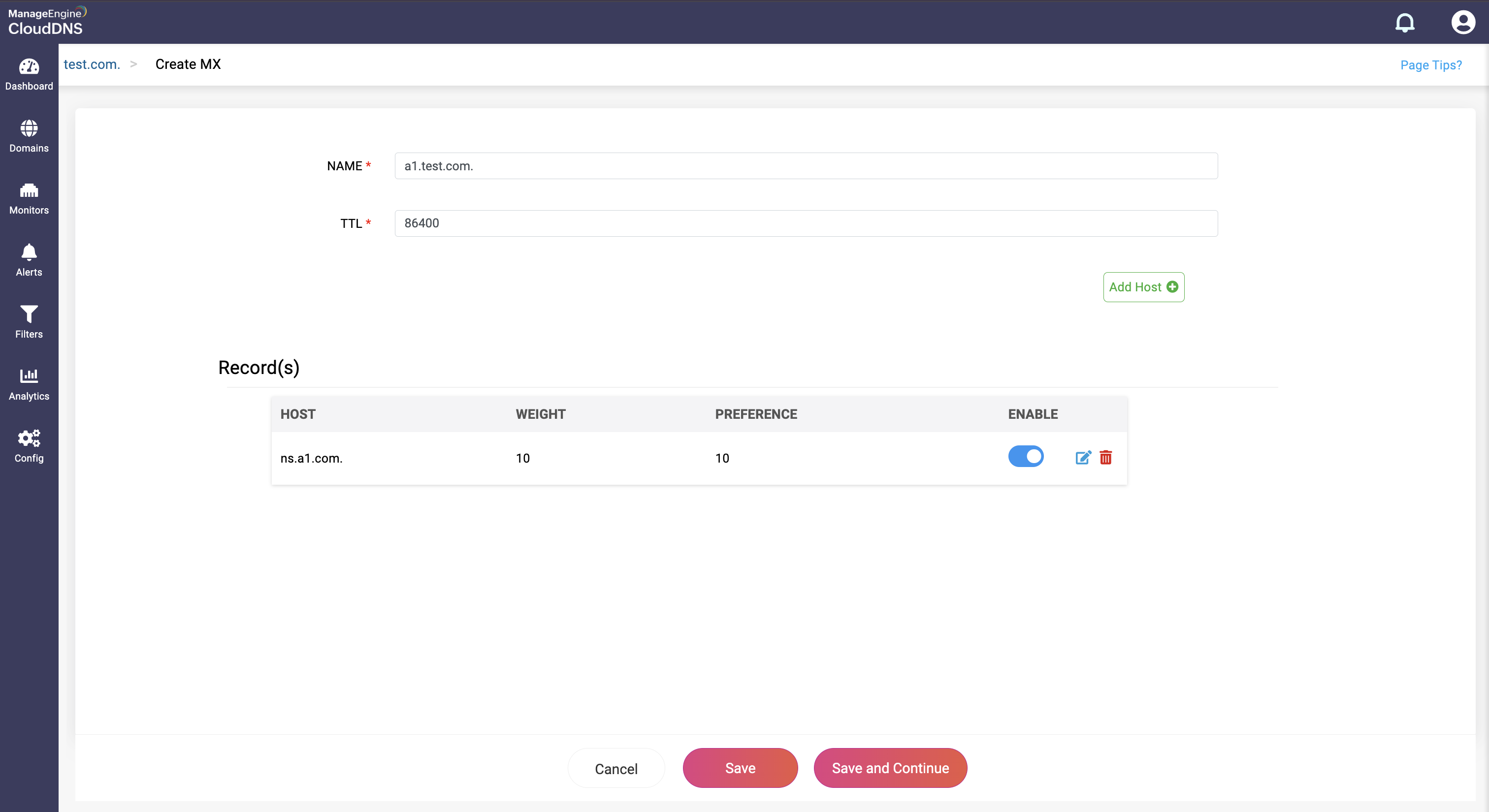
Step 4: Proceed to save the record by clicking on "Save" or "Save and Continue" to keep adding more entries to the record.
What is a NS record
Name Server (NS) records are responsible for indicating which servers should be answering DNS queries from a specific domain. They identify the name servers holding DNS records of that domain, and basically direct DNS queries to the appropriate authoritative name servers, thus enhancing the network services of an organization.
How do you create a NS record?
Step 1: On the Domains page, click on a domain name of your choice to access its records. Navigate to the NS record section.
Step 2: On the right side, you can view a "+" sign for adding a record, and a "-" sign for deleting a record. Click the "+" sign to add a new NS record.
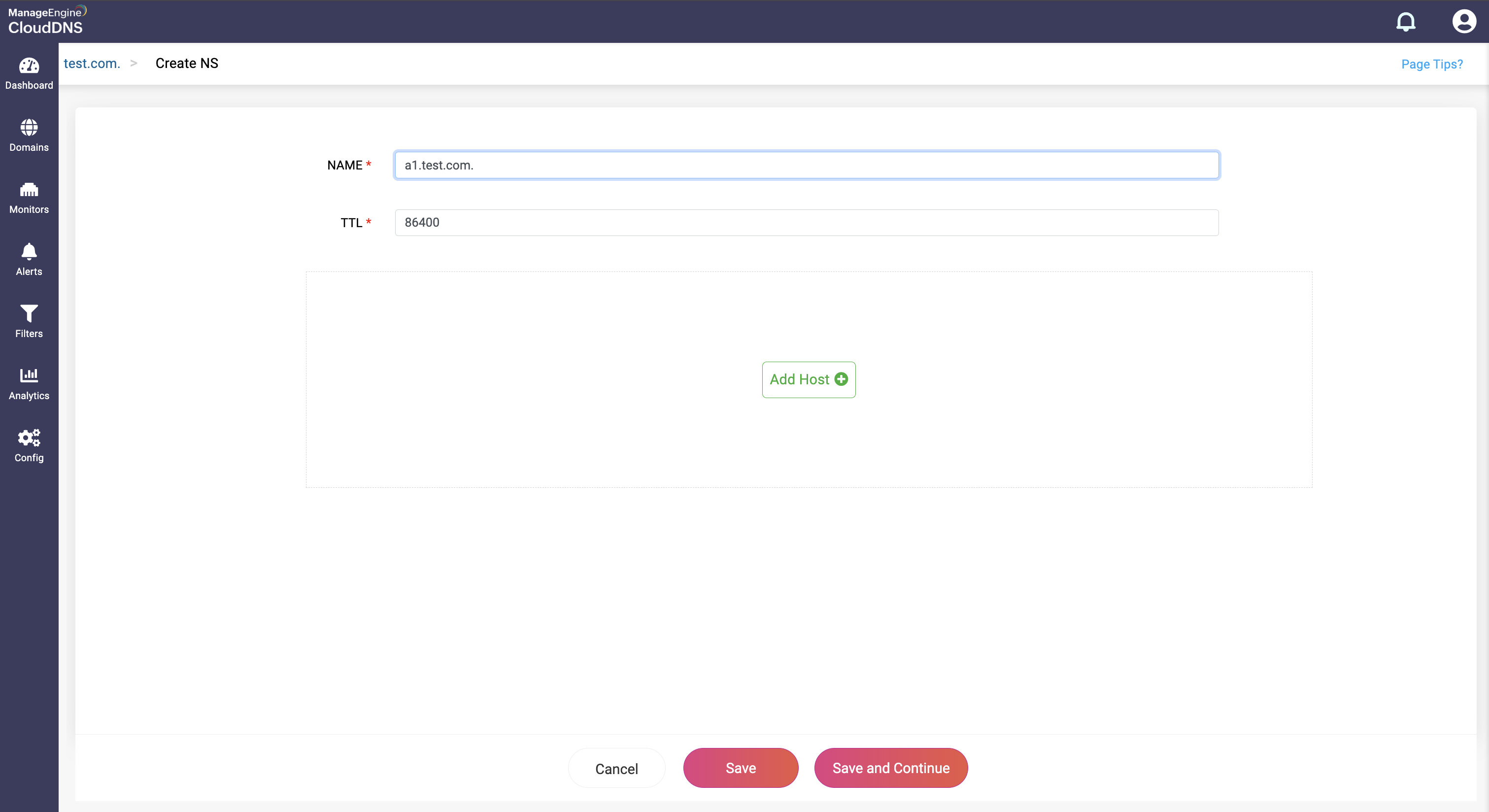
Step 3: Provide the details of the new NS record, such as name, TTL, date and time.
Provide the domain name of the authoritative name server in the Host field.
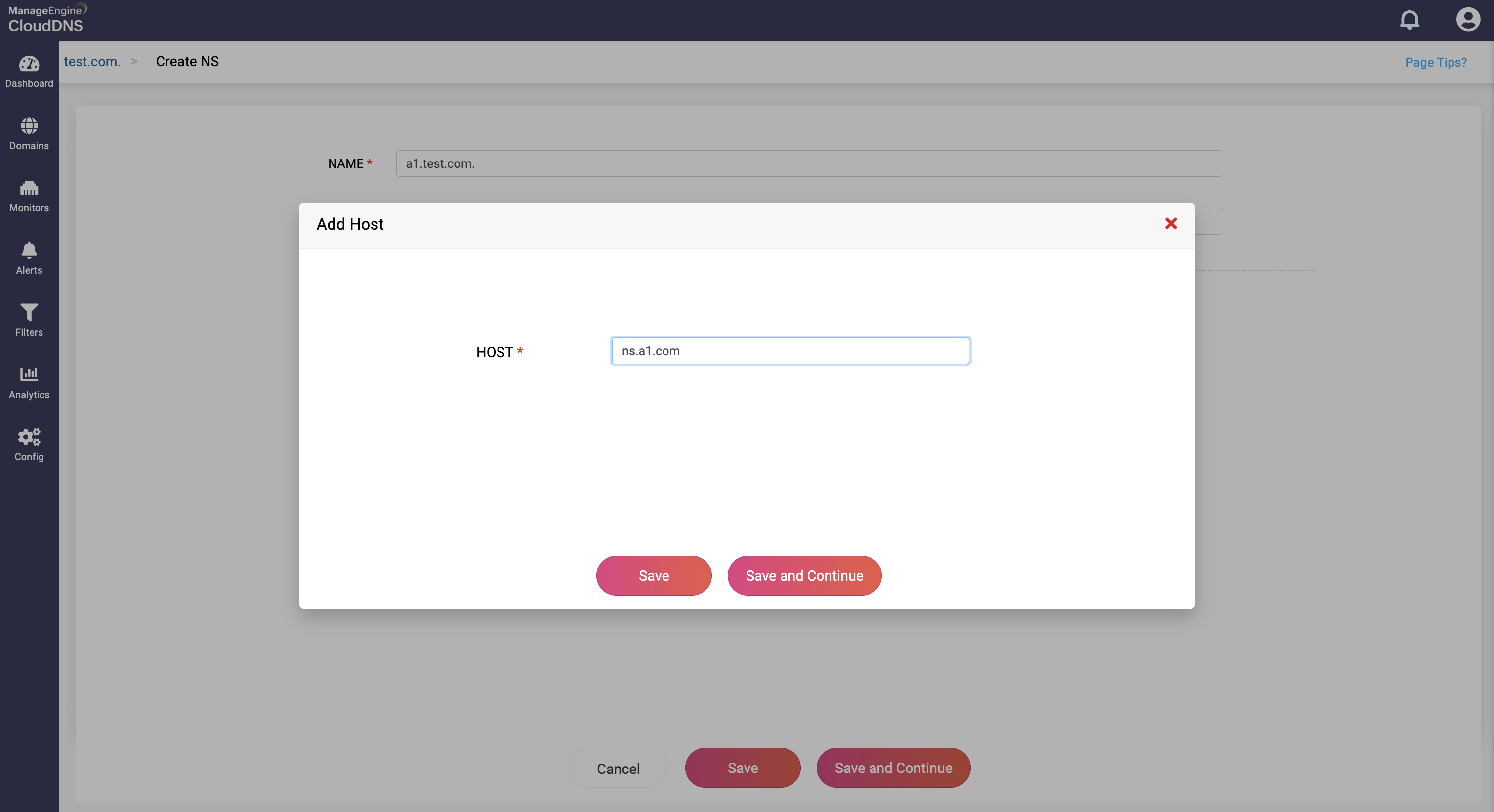
Step 4: Proceed to save the record by clicking on "Save" or "Save and Continue" to keep adding more entries to the record.
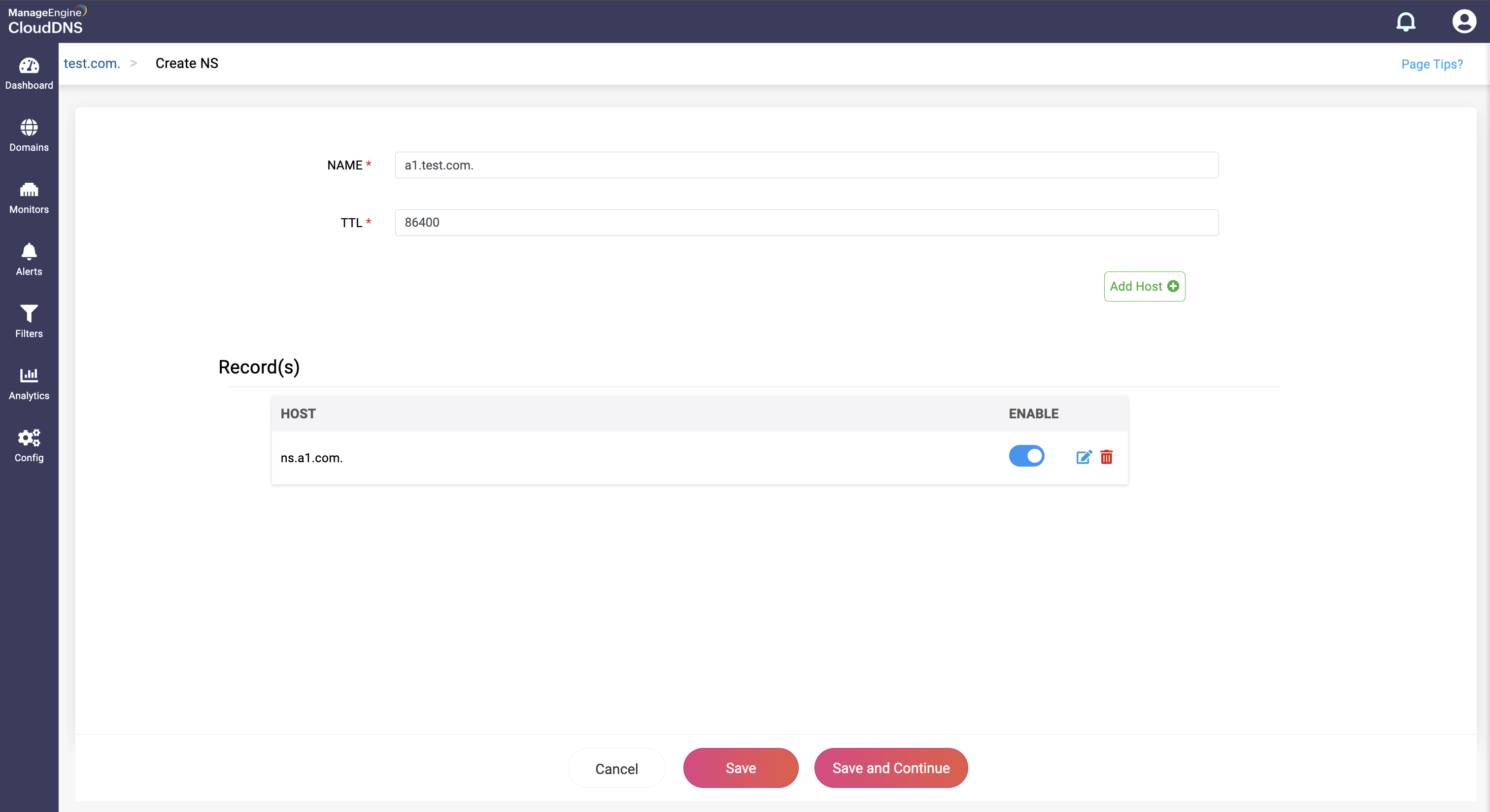
Note: If you have given the name server of the same domain, for ex: "ns.example.com" is the name server of "example.com", then the domain name must have an A record (IPv4) or an AAAA record (IPv6) for BIND to respond, otherwise BIND will respond with error when there is no A or AAAA record.
What is a PTR record
Pointer (PTR) records function in the opposite way compared to the A records. They map IP addresses to the respective domain names. PTR records are primarily used in the reverse DNS lookups for email verification, host and device identification, security and authentication purposes. This ensures that an IP address is associated with the right domain name.
How do you create a PTR record?
Step 1:On the Domains page, click on a domain name of your choice to access its records. Navigate to the PTR record section.
Step 2: On the right side, you can view a "+" sign for adding a record, and a "-" sign for deleting a record. Click the "+" sign to add a new PTR record.

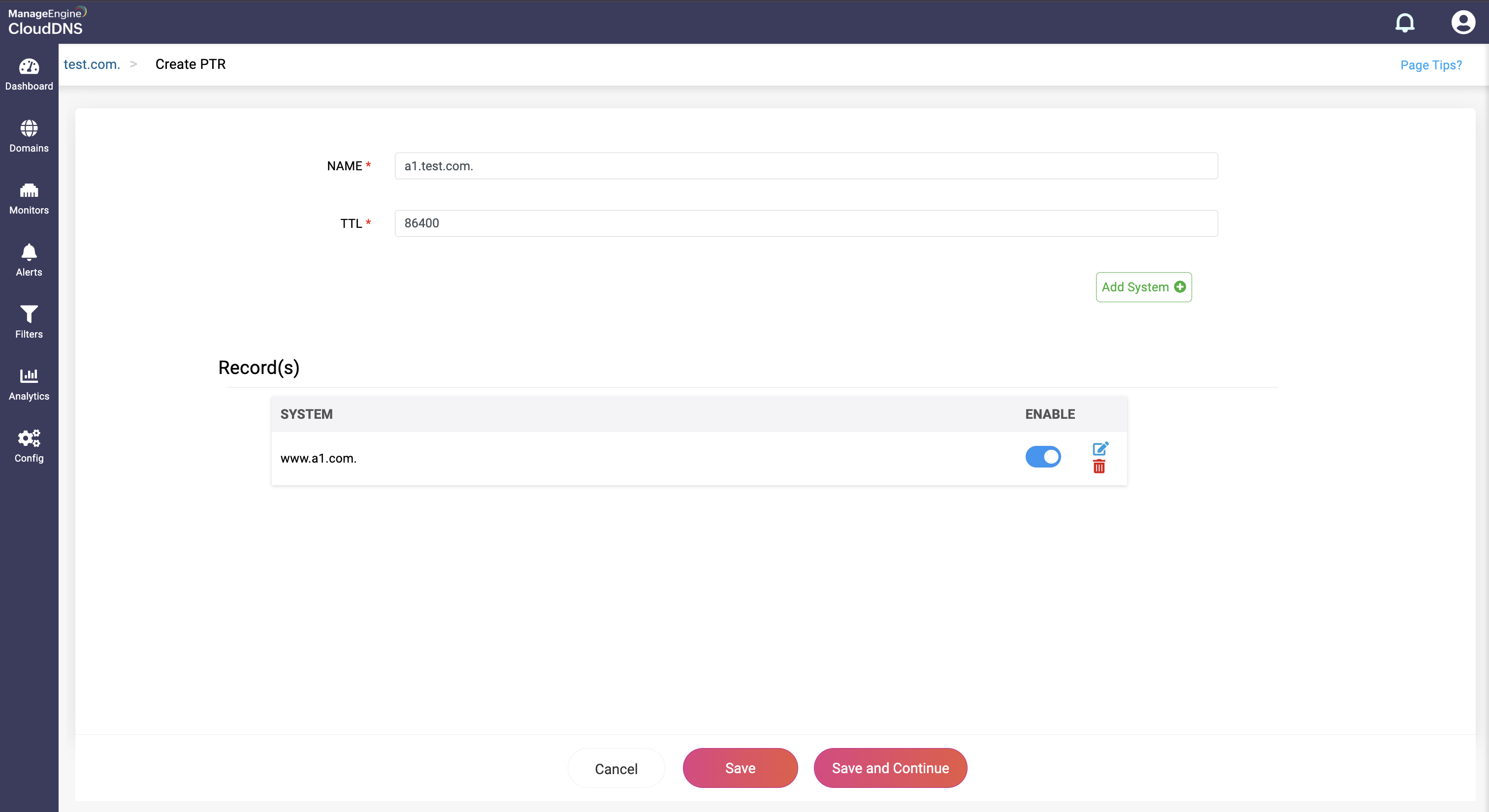
Step 3: Provide the details of the new PTR record, such as name, TTL, date and time.
Provide the domain name the IP address should map to in the System field.
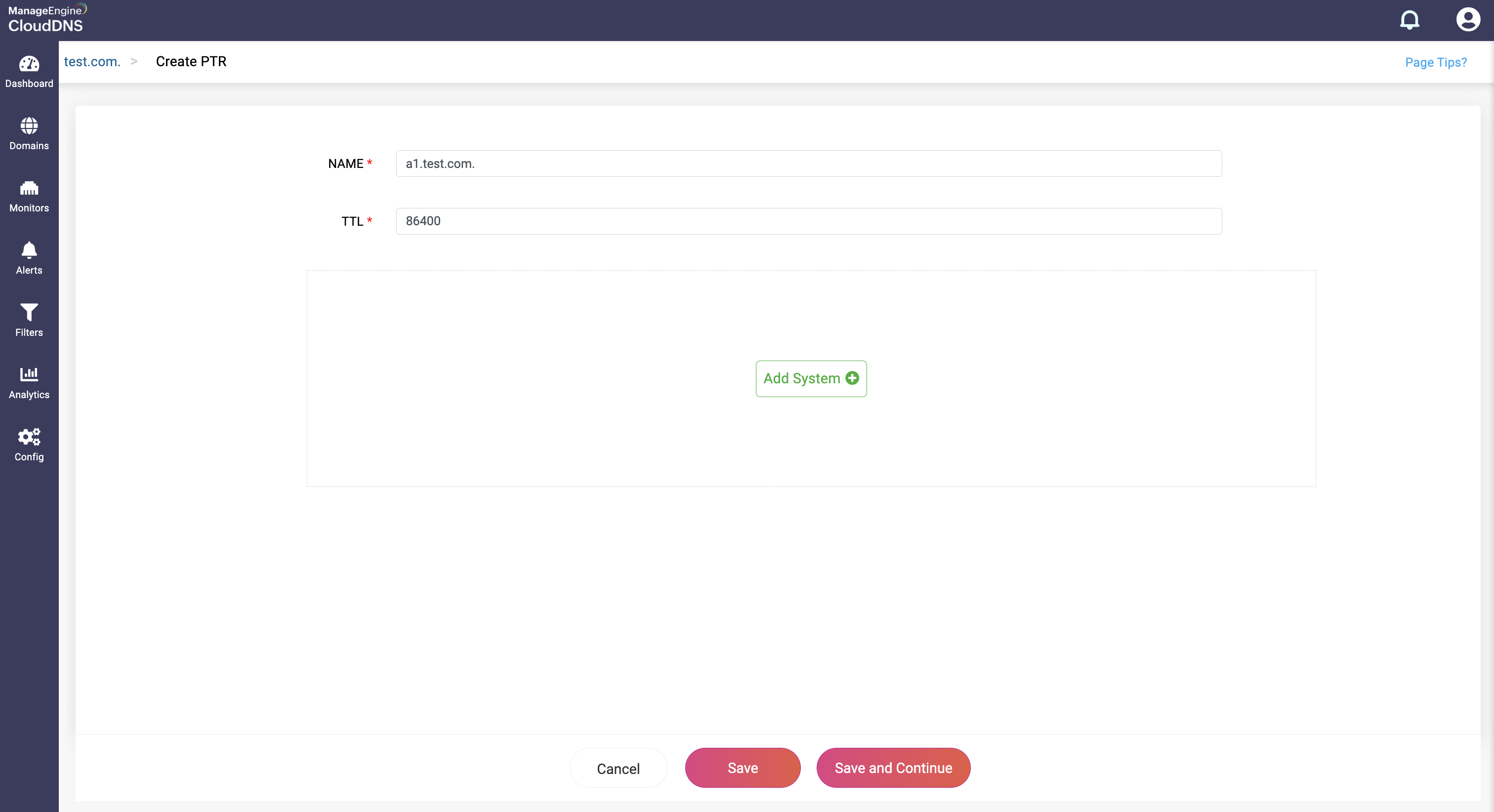
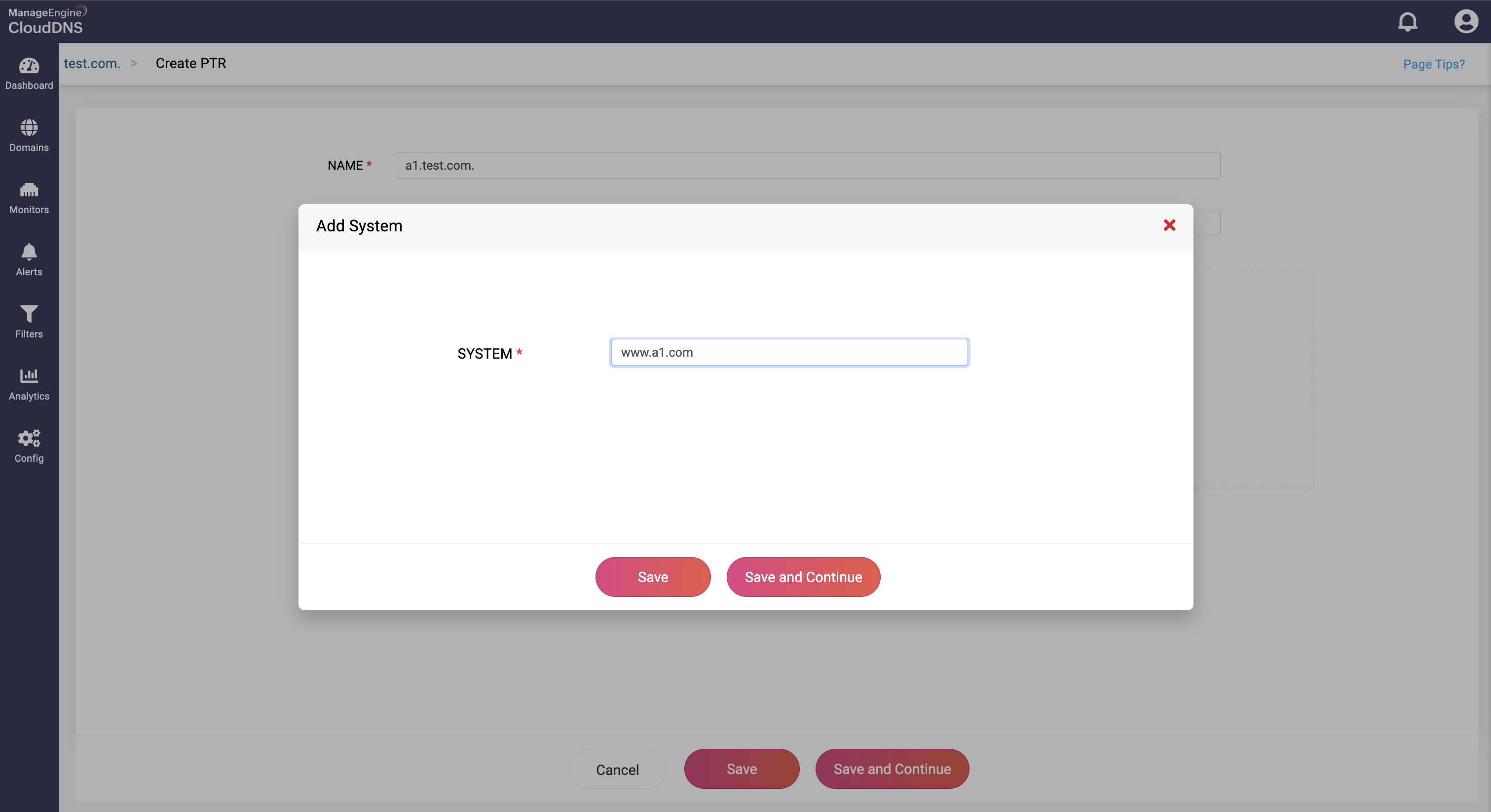
Step 4: Proceed to save the record by clicking on "Save" or "Save and Continue" to keep adding more entries to the record.
What is a SPF record
Sender Policy Framework (SPF) records specify which mail servers are authorized to send mails of a domain name. SPF records help domain owners create a list of authorized hostnames and IP addresses that are permitted to send email from their domain. They are used to enhance email communications and security by preventing email spoofing, email spam, and phishing attacks.
How do you create a SPF record?
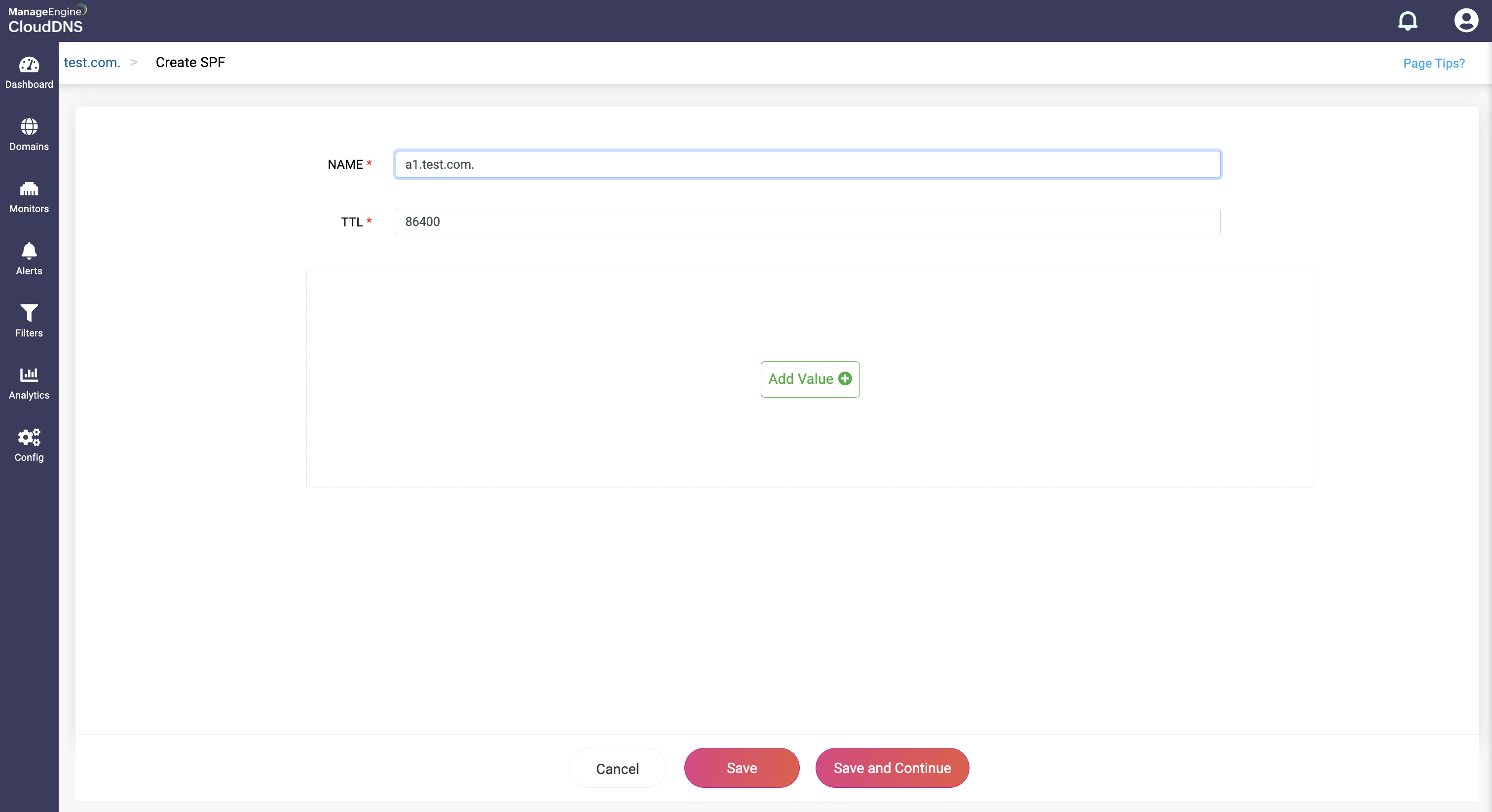
Step 1: On the Domains page, click on a domain name of your choice to access its records. Navigate to the SPF record section.
Step 2: On the right side, you can view a "+" sign for adding a record, and a "-" sign for deleting a record. Click the "+" sign to add a new SPF record.
Step 3: Provide the details of the new SPF record, such as name, TTL, date and time.
Provide the SPF policy in the Value field for email authentication. The policy specifies which mail servers are authorized to send email on behalf of the domain and can include various mechanisms and qualifiers.
The value you've given will be listed in the Entered Value drop-down field.
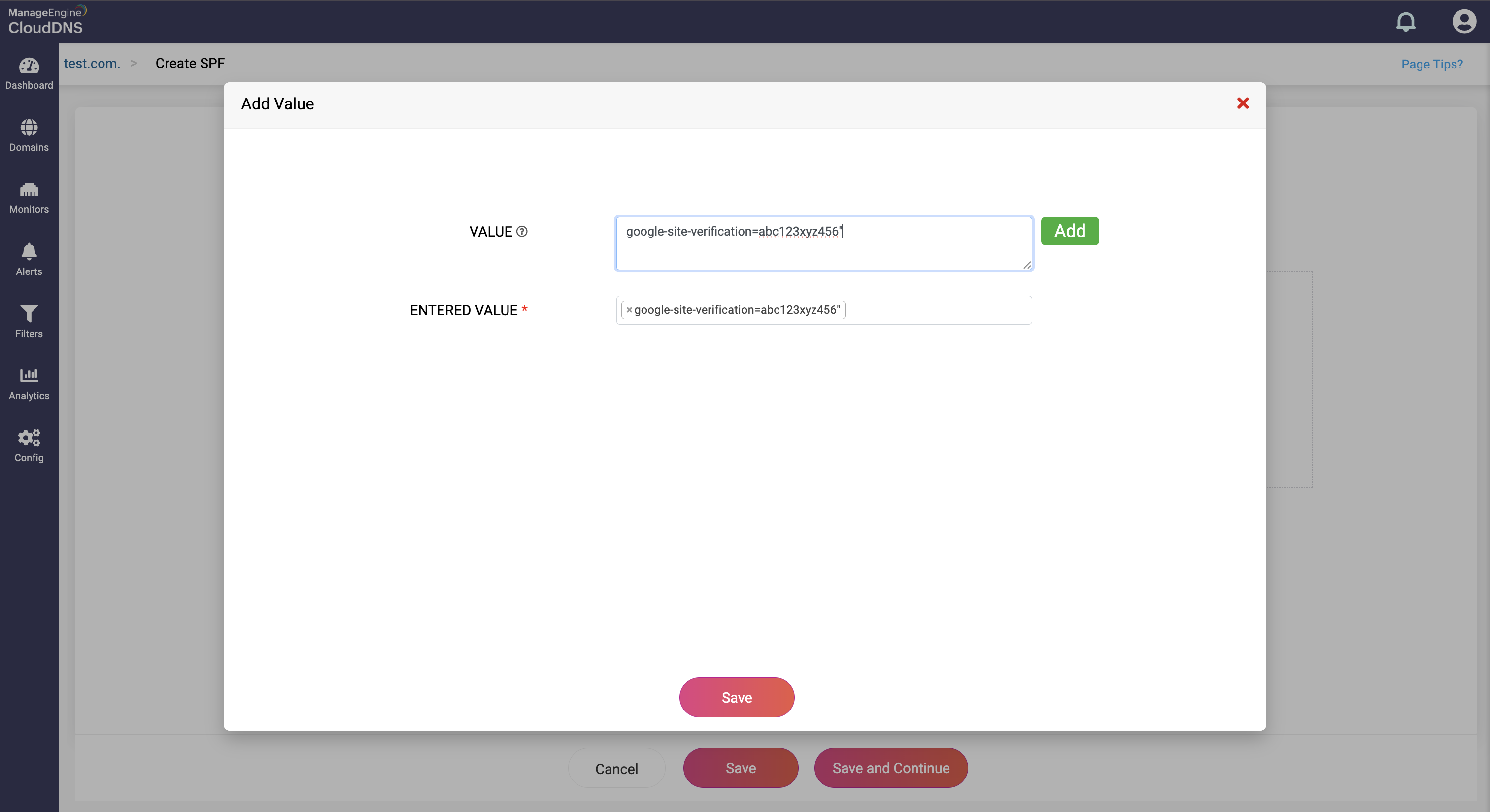
Step 4: Proceed to save the record by clicking on "Save" or "Save and Continue" to keep adding more entries to the record.
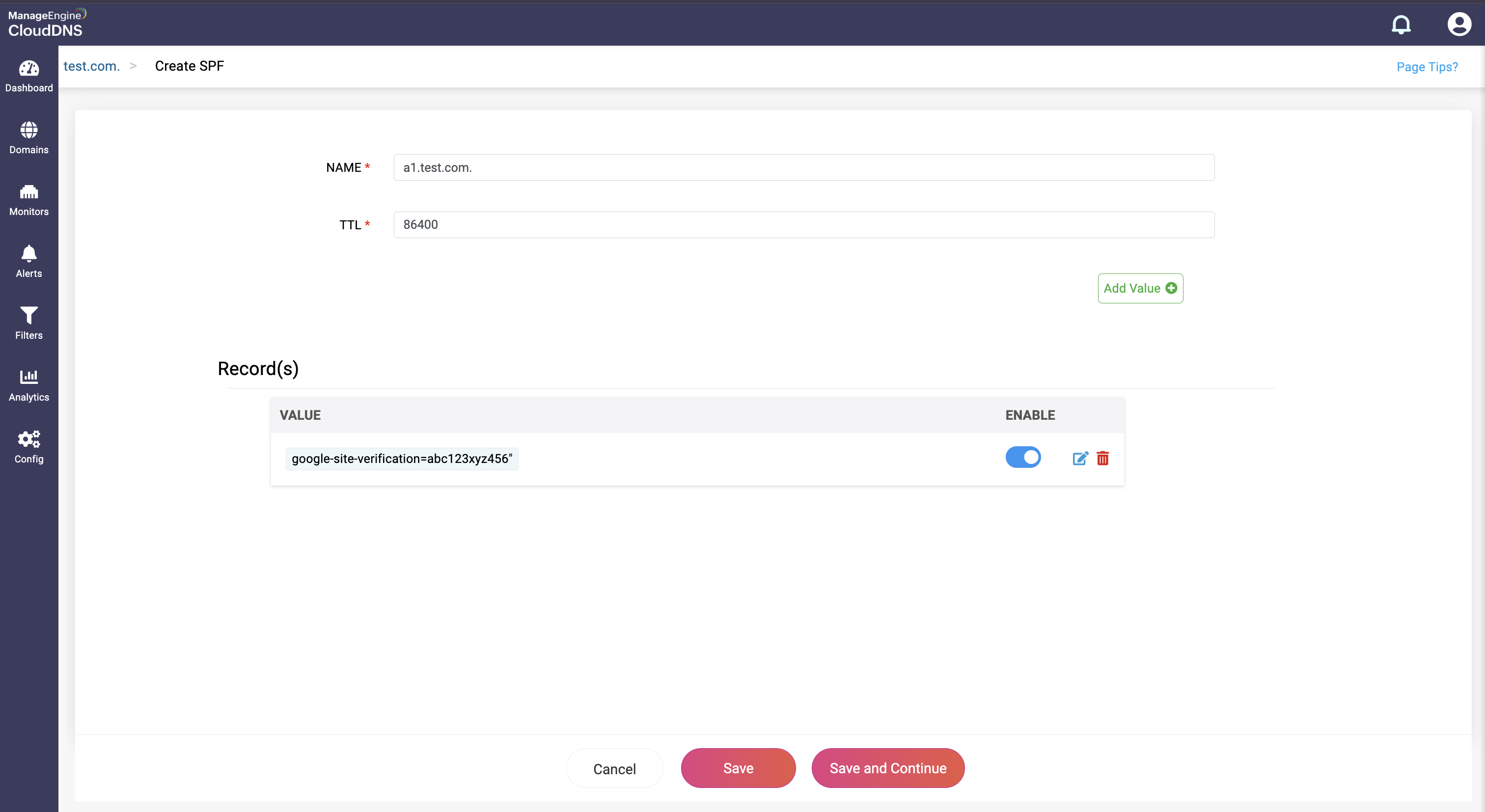
Note: SPF record has a value limit of 256 characters, if the value exceeds 256 characters, then have to given separately in double quotes, ex: "val1""val2".
What is a SRV record
Service (SRV) records are used to locate the right servers for specific queries. They provide the details of the hostname and port numbers of the servers, allowing clients to connect with specific services easily. SRV records facilitate service discovery and seamless connection for clients, thus offering flexibility, load balancing, and failover management.
How do you create a SRV record?
Step 1:On the Domains page, click on a domain name of your choice to access its records. Navigate to the SPF record section.
Step 2: On the right side, you can view a "+" sign for adding a record, and a "-" sign for deleting a record. Click the "+" sign to add a new SRV record.
Step 3: Provide the details of the new SRV record, such as name, TTL, date and time. There are three fields in the Add Host field.
- Target: This field contains the domain name of the target host providing the service. The target must point to a domain name with an A or an AAAA record, not directly to an IP address.
- Port: This field specifies the port number on which the target server is listening for the service.
- Weight: This field is an integer value used to distribute the load between servers with the same priority. Higher values are given proportionately more traffic. If multiple servers have the same priority, the weight field determines the distribution of requests.
- Priority: This field is an integer value that indicates the priority of the target server. Lower values have higher priority. Clients try to contact the server with the lowest priority first.
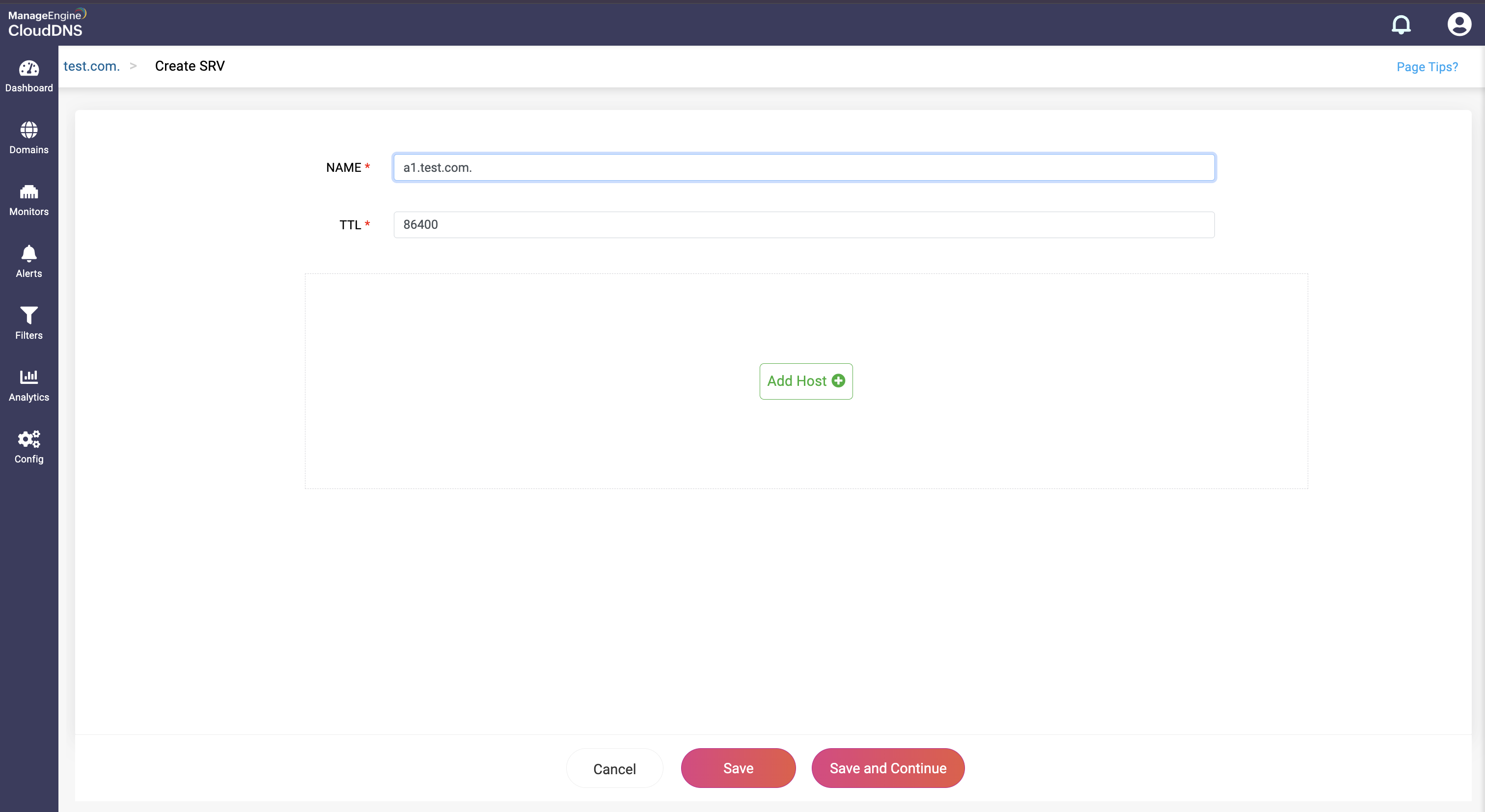
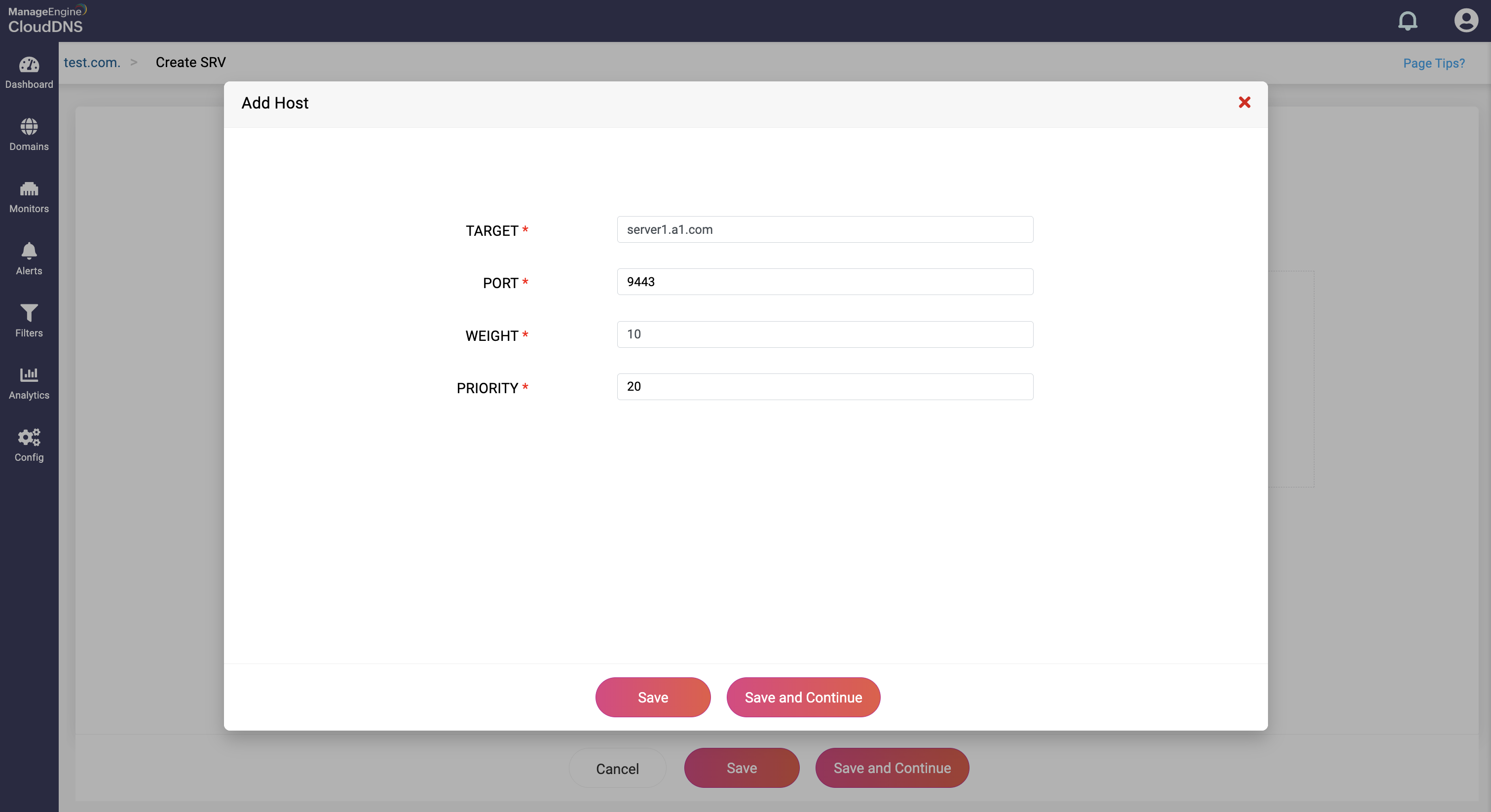
Step 4: Proceed to save the record by clicking on "Save" or "Save and Continue" to keep adding more entries to the record.
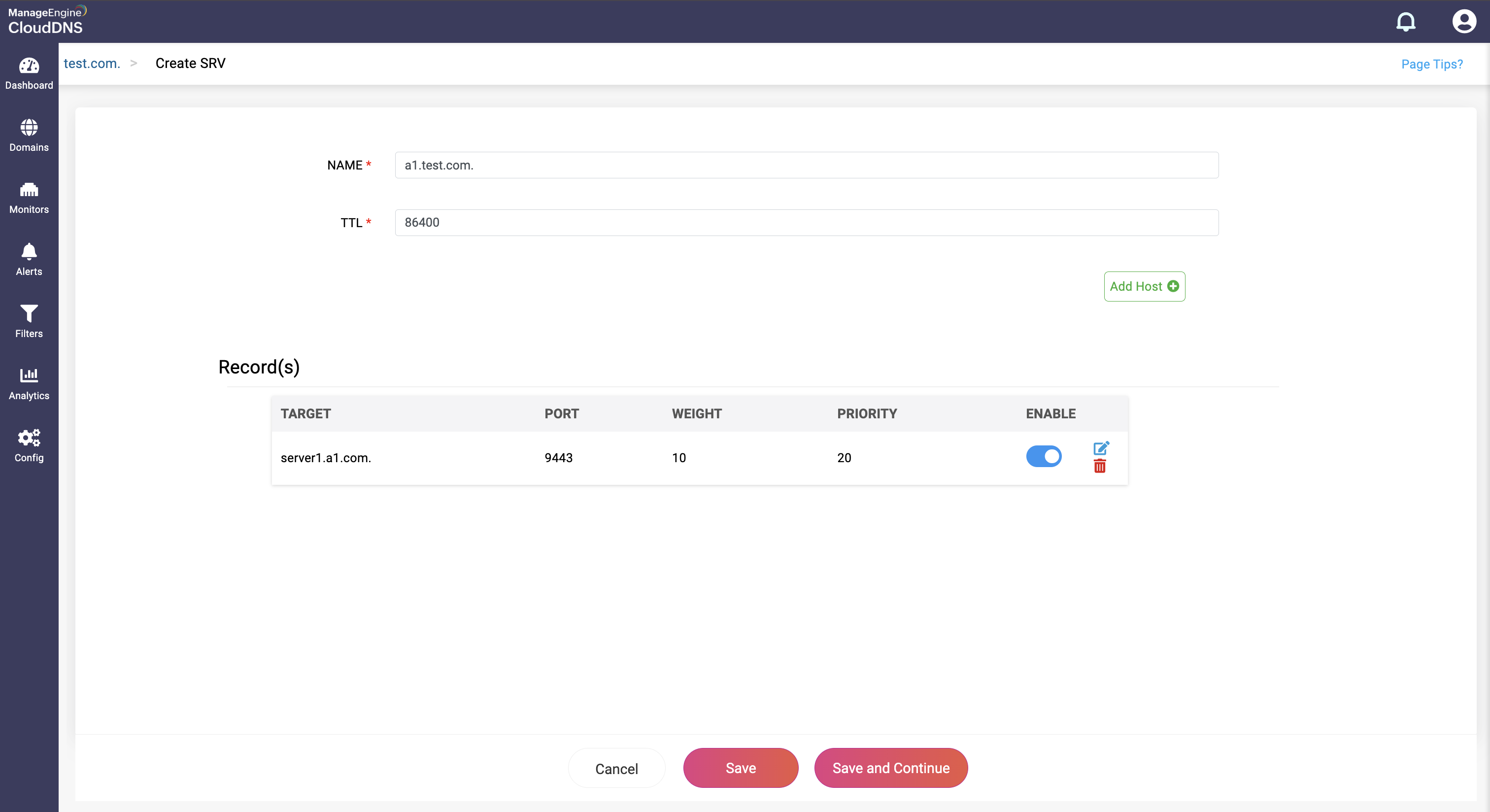
What is a TLSA record
Transport Layer Security Authentication (TLSA) record is used for DANE (DNS-based Authentication of Named Entities). It links a domain and port to a specific TLS certificate or public key, allowing clients to verify the certificate via DNS instead of relying solely on certificate authorities (CAs). This enhances trust and security, especially in email (SMTP) or internal systems.
How do you create a TLSA record?
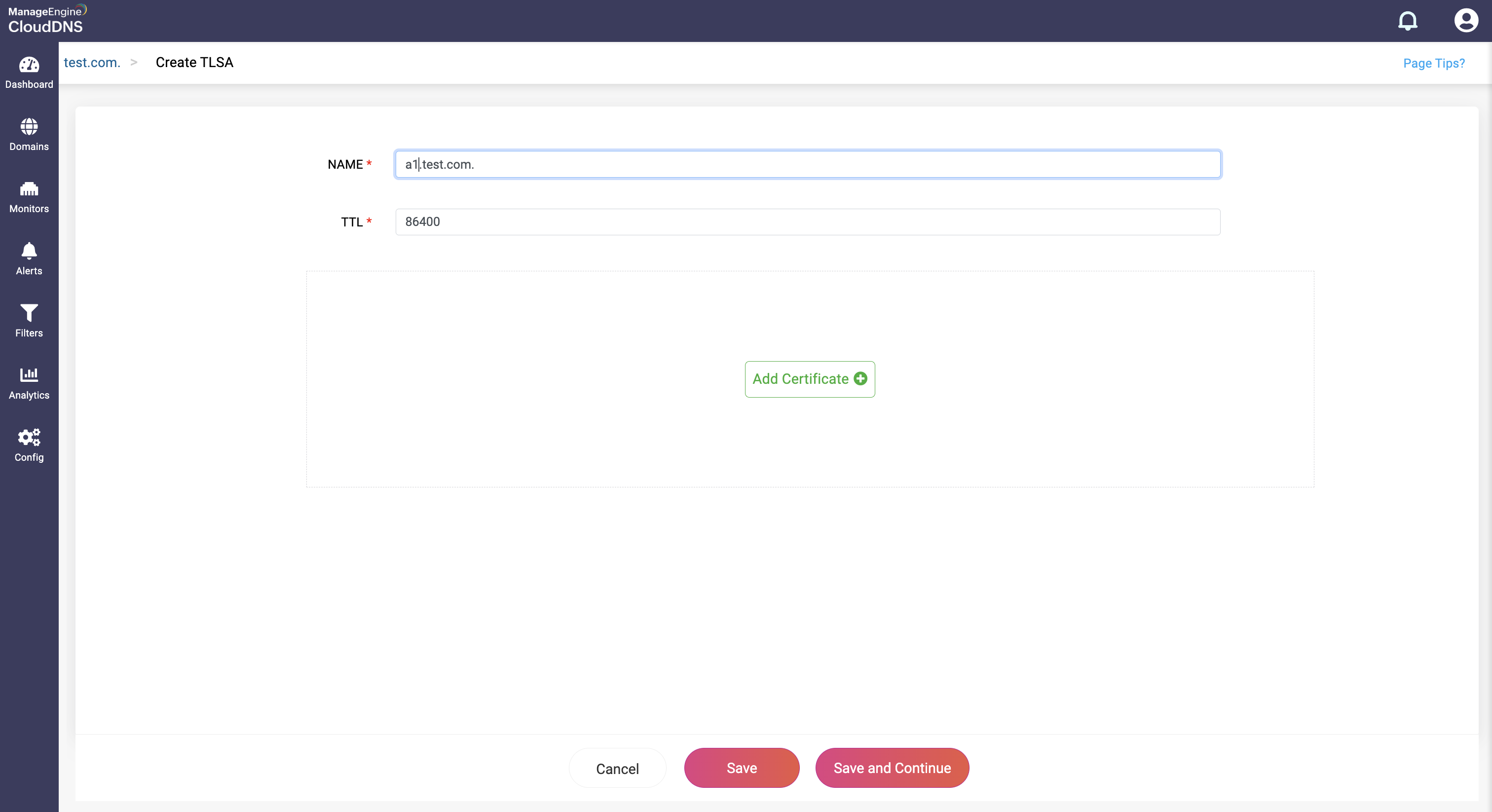
Step 1: On the Domains page, click on a domain name of your choice to access its records. Navigate to the TLSA record section.
Step 2: On the right side, you can view a "+" sign for adding a record, and a "-" sign for deleting a record. Click the "+" sign to add a new TLSA record.
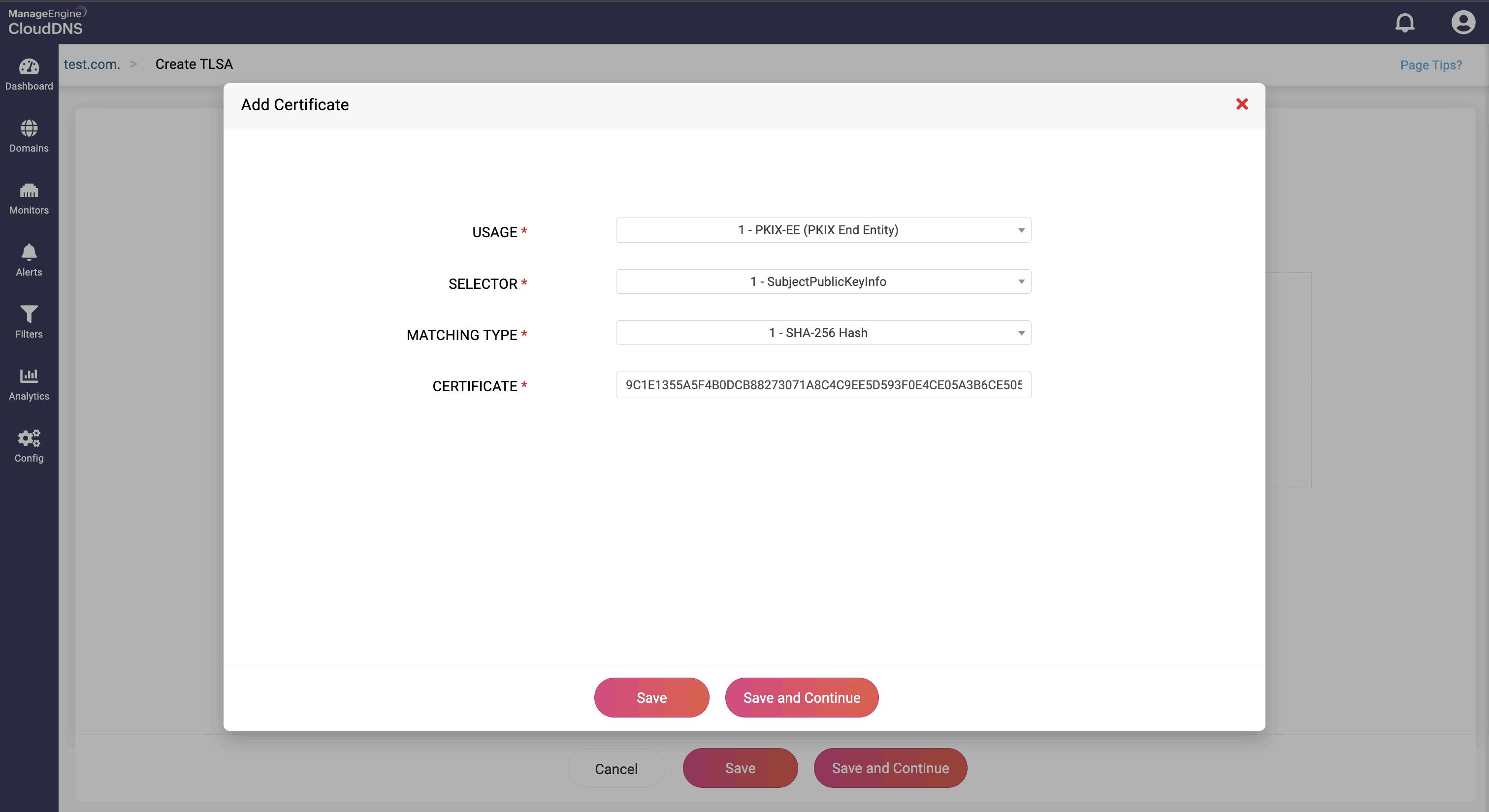
Step 3: Provide the details of the new TLSA record, such as name, TTL, date and time. Ther are four fields in Add Certfificate ssection:
- Usage: Tells the client what kind of certificate is being validated
- Selector: Specifies which part of the certificate is used (full or SPKI)
- Matching type: Defines how the certificate data is encoded (raw or hashed)
- Certificate value: The actual data to match (raw bytes or hex-encoded hash)
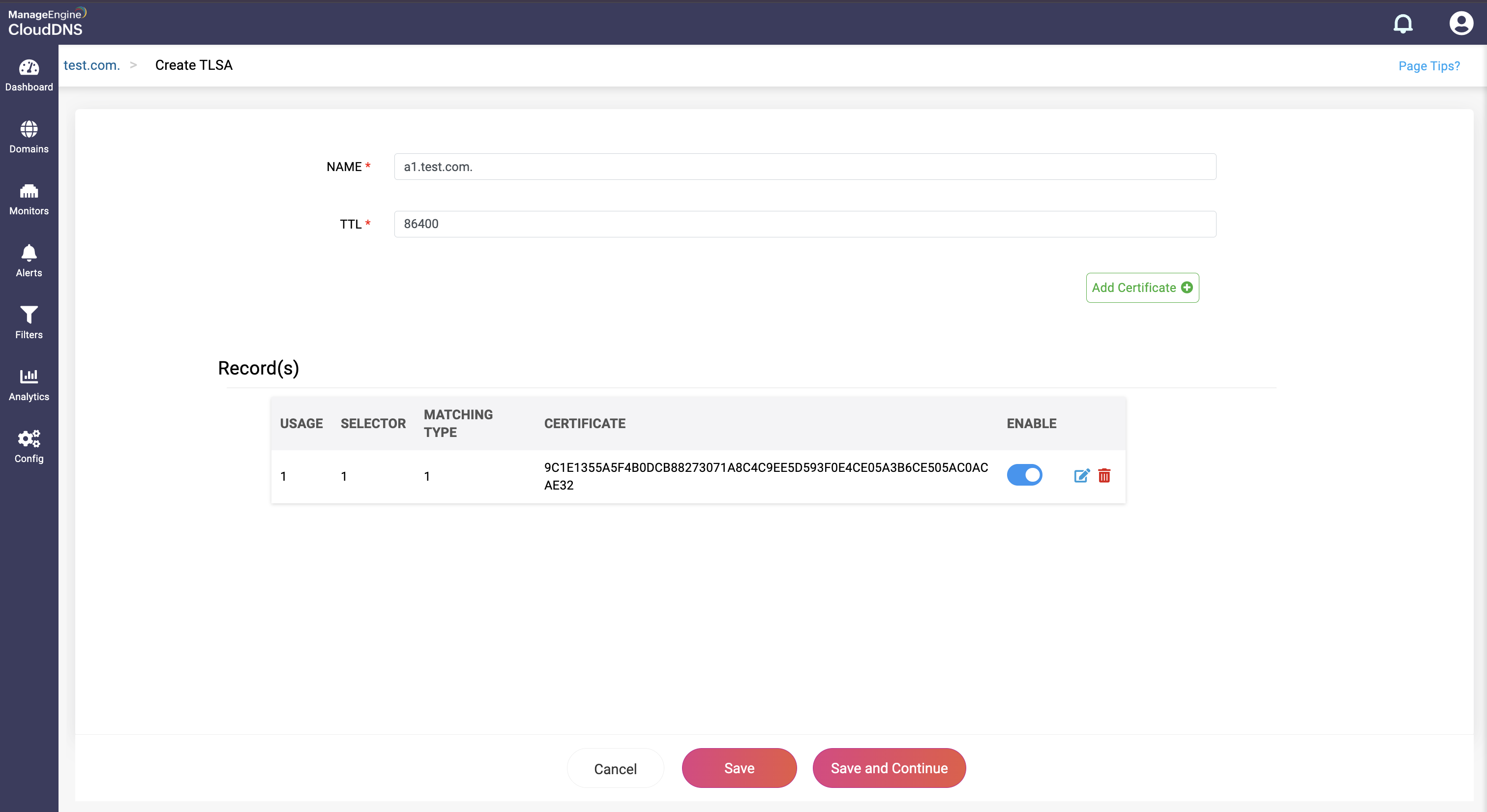
Step 4: Proceed to save the record by clicking on "Save" or "Save and Continue" to keep adding more entries to the record.
What is a TXT record
Text (TXT) records allows network administrators to insert text information into any DNS response. These records contain various types of data and are mostly used for email security and domain ownership verification. For email security, TXT records are used to store public keys in the mail server and are used to digitally sign an email as well as define policies for handling mails that fail Sender Policy Framework (SPF) checks. For domain ownership verification, TXT records are used to prove domain ownership by adding specific value provided by the service into the domain's DNS record.
How do you create a TXT record?
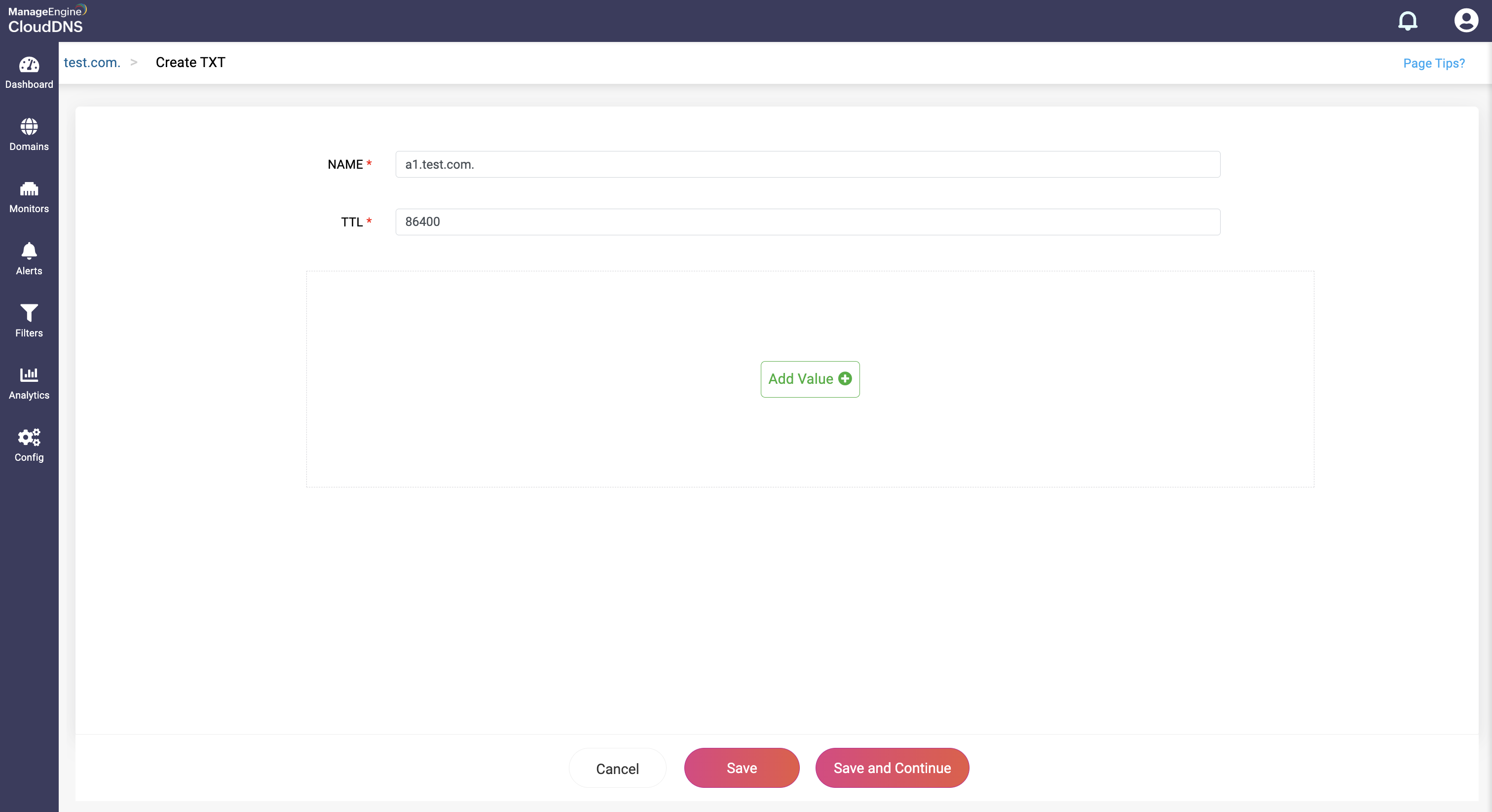
Step 1: On the Domains page, click on a domain name of your choice to access its records. Navigate to the TXT record section.
Step 2: On the right side, you can view a "+" sign for adding a record, and a "-" sign for deleting a record. Click the "+" sign to add a new TXT record.
Step 3: Provide the details of the new TXT record, such as name, TTL, date and time. There are two fields in the Add Value section.
Value: This field contains the actual text data associated with the record. The content of the value field is arbitrary text, often used for various purposes such as verification, authentication, or informational text.
The value you've given will be listed in the Entered Value dropdown field.
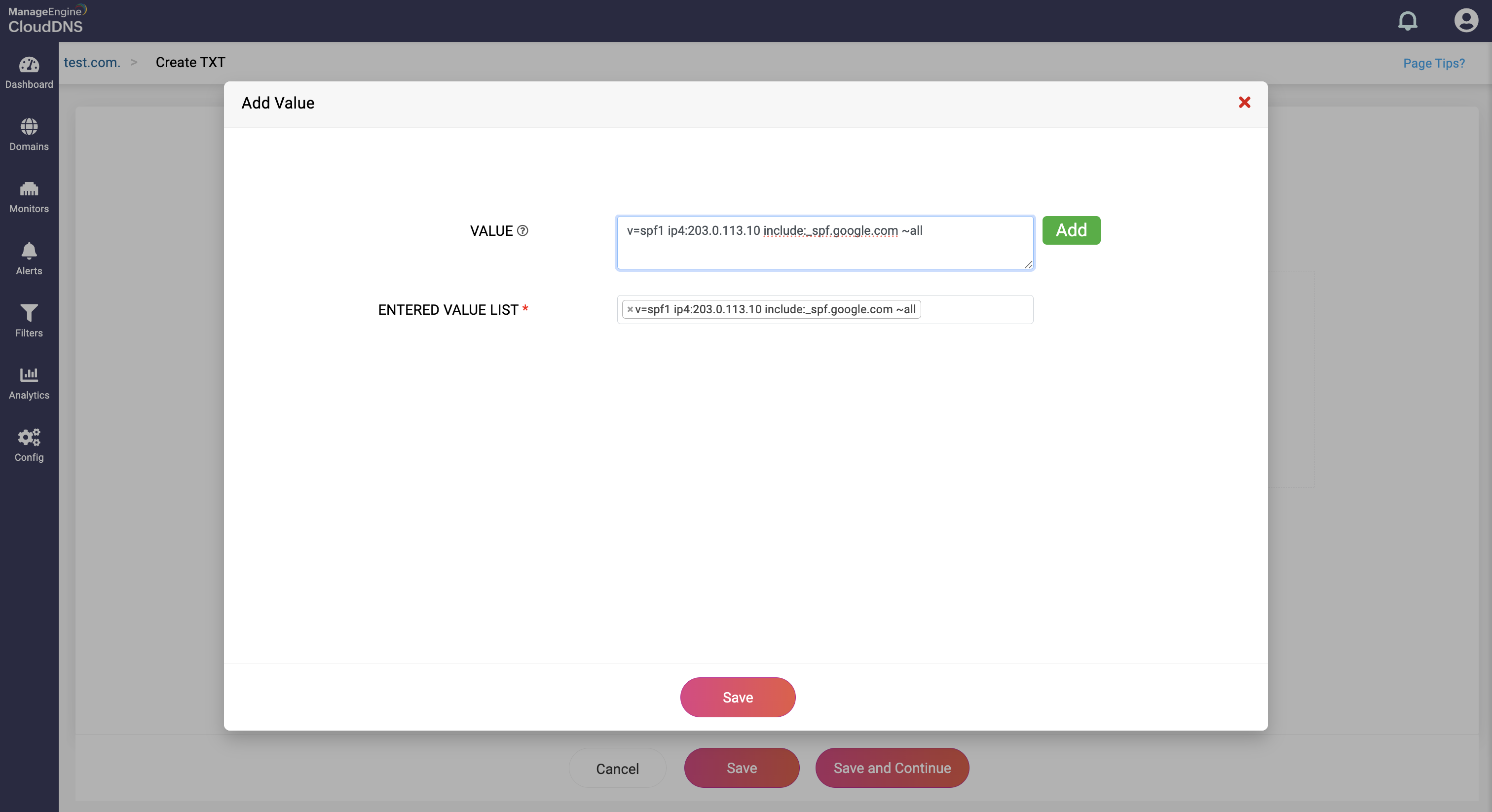
Step 4: Proceed to save the record by clicking on "Save" or "Save and Continue" to keep adding more entries to the record.
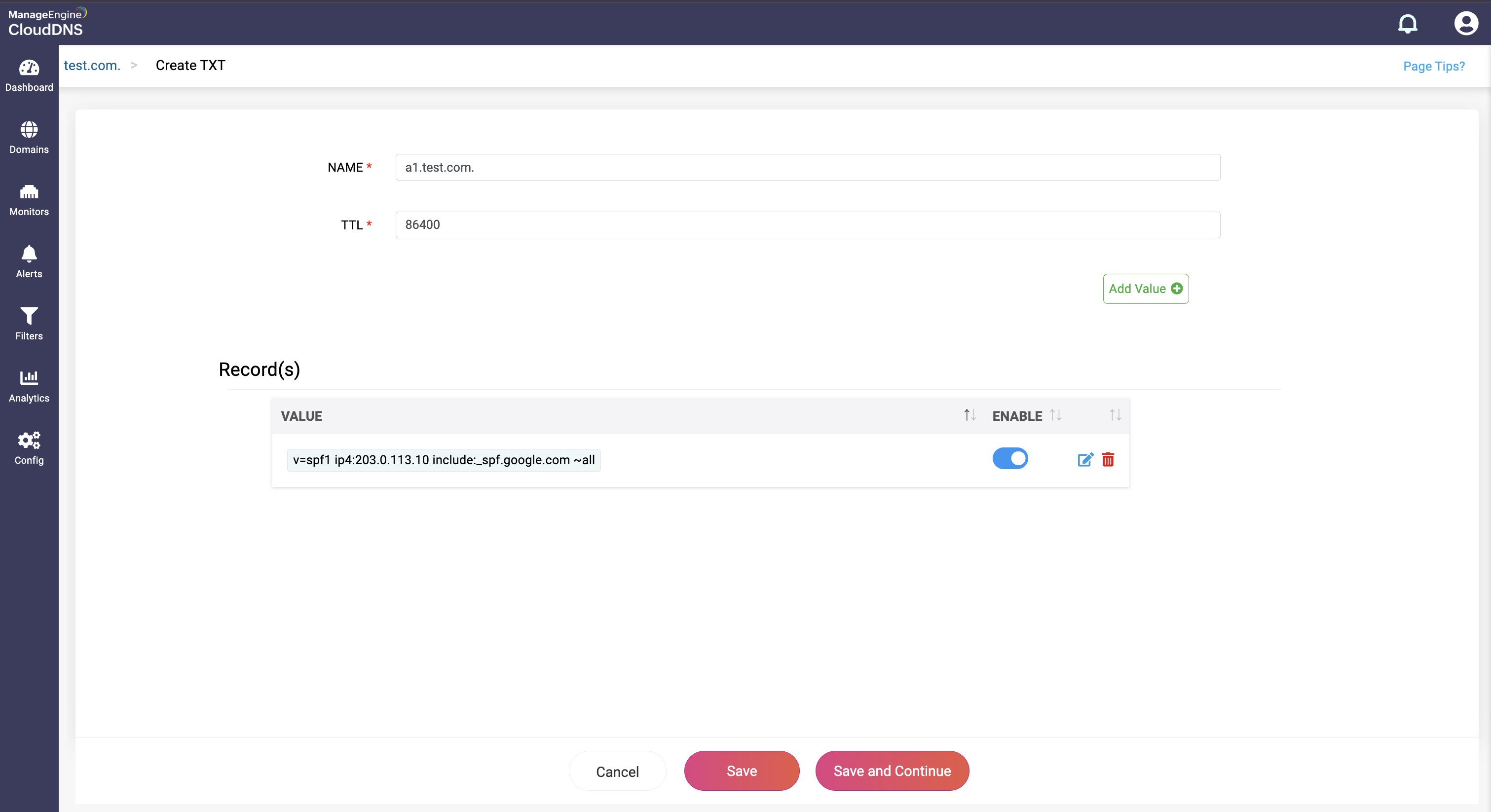
Note: SPF record has a value limit of 256 characters, if the value exceeds 256 characters, then have to given separately in double quotes, ex: "val1""val2".
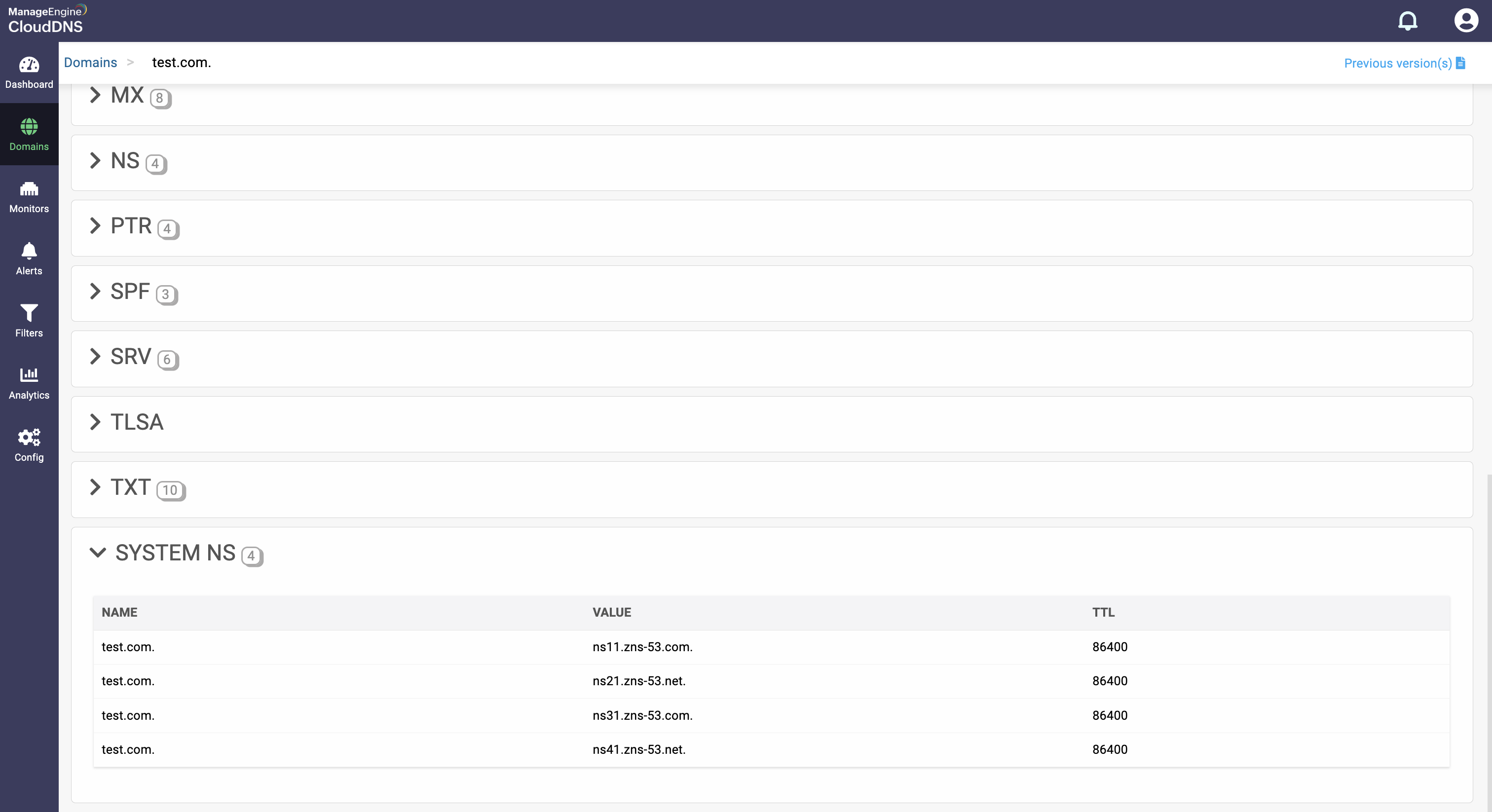
What is a SYSTEM NS record
System NS refers to the authoritative name servers assigned to a domain. These are the DNS servers responsible for answering queries about that domain, such as IP addresses for websites or mail servers. The NS (Name Server) records define which servers hold the DNS zone for the domain, and “system NS” typically means the default or primary name servers provided by your DNS hosting provider.
New to ADSelfService Plus?
Related Articles
DNS records setup in ManageEngine CloudDNS
How to create and update DNS records? What is a DNS record? The DNS records (also known as zone files or resource records) are the constituent files of a Zone or a Domain that carry the essential instructions that help the DNS resolver quickly ...DNS monitoring in ManageEngine CloudDNS
DNS monitoring in ManageEngine CloudDNS DNS monitoring in CloudDNS is crucial to ensure the health and performance of your DNS infrastructure. By configuring DNS monitors in CloudDNS, you can keep a constant eye on your DNS servers and records. It is ...Guide to DNS records
The following are the types of resource records supported by ManageEngine CloudDNS: A (IPv4): Address record that maps a domain name to an IPv4 address, allowing a domain to be associated with a physical machine or resource on an IPv4 network. AAAA ...How to configure vanity nameservers in ManageEngine CloudDNS
What are vanity nameservers? Vanity nameservers enable organizations to rebrand CloudDNS's public nameservers by branding them to a domain of their choice, masking CloudDNS as the original host or DNS provider. Vanity nameservers are configured in ...Zone Transfers in ManageEngine CloudDNS
Configuring ManageEngine CloudDNS as a primary DNS provider If your organization works with multiple DNS providers you can deploy CloudDNS as the primary provider, in parallel with other third-party primary or secondary DNS providers. Under this ...