Configuring Response Rate Limiting execution
Configuring RRL Exception List for Microsoft DNS
Response Rate Limiting (RRL) helps mitigate the effects of DNS amplification attacks by limiting the rate at which responses are sent to clients. However, there might be certain clients or subnets that you want to exempt from these limits. Configuring an RRL exception list allows you to specify such exemptions.
The image below illustrates how an RRL exception list is configured for Microsoft DNS using DDI Central.
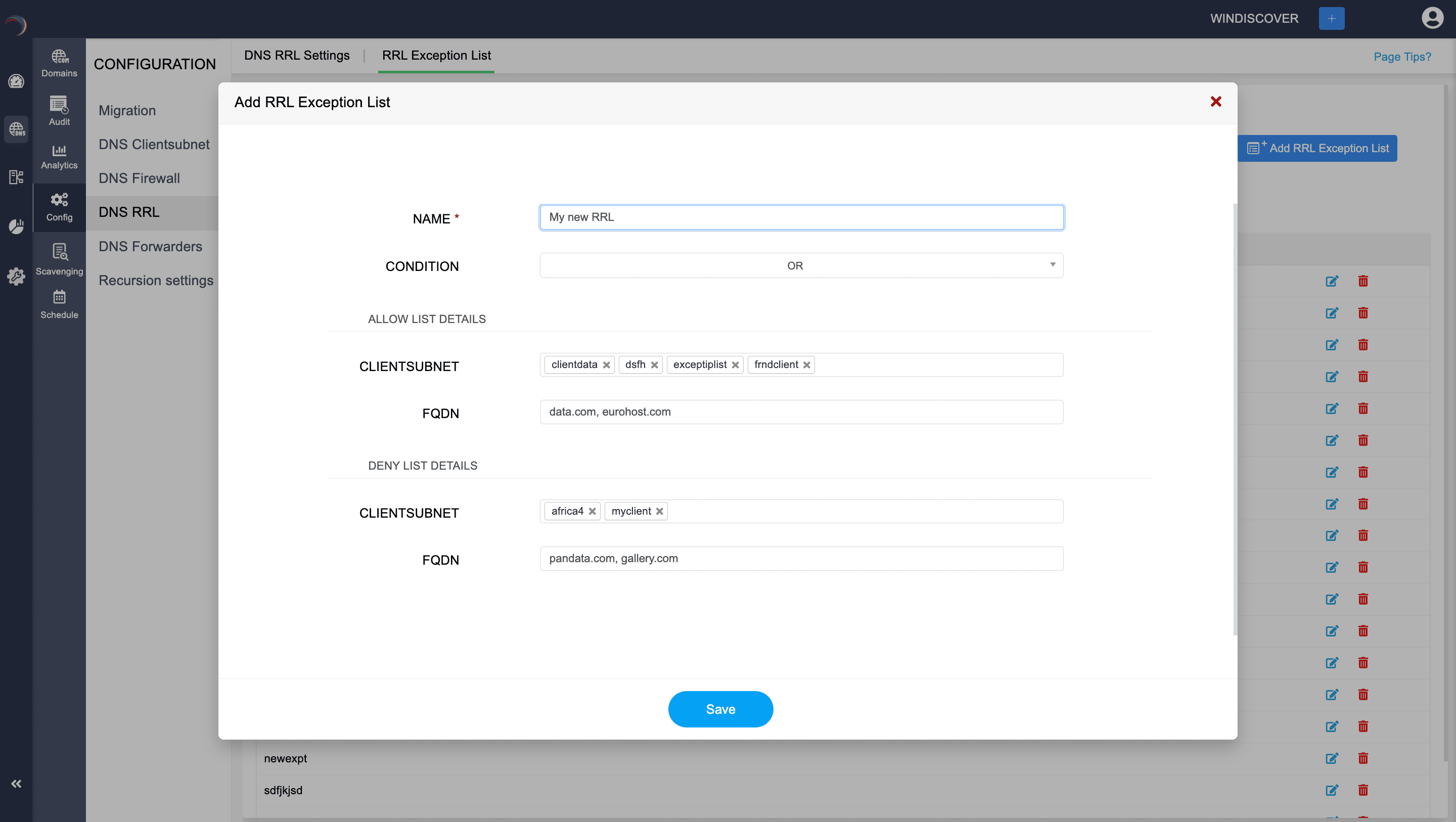
Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to configure it:
- NAME: Assign a unique name for the new exception list. This helps to quickly identify the exception rule.
- CONDITION: Select the logical condition to apply for the exception (AND/OR). It is this logical operator that determines how multiple criteria (subnets and FQDNs) should be evaluated for the exception.
- ALLOW LIST DETAILS:
- CLIENTSUBNET: Select the subnets from the list of configured clientsubnets that should be exempted from RRL.
- FQDN: Specify the FQDNs that should be exempted from RRL. Use a comma to separate multiple entries.
- DENY LIST DETAILS:
- CLIENTSUBNET: Select the client subnets that should not be exempted from RRL.
- FQDN: Specify the FQDNs that should not be exempted from RRL. Use a comma to separate multiple entries.
- Click Save to apply the exception list settings.
By following these steps, you can effectively manage RRL exceptions in Microsoft DNS, ensuring that trusted clients and critical services are not impacted by rate limiting, while still protecting your DNS infrastructure from potential abuse.
New to ADSelfService Plus?
Related Articles
Configuring Response Rate Limiting settings
Configuring DNS Response Rate Limiting (RRL) settings Response Rate Limiting (RRL) is a security feature designed to mitigate the impact of DNS amplification attacks by limiting the rate of responses a DNS server can send to a client. Configuring RRL ...Response rate limiting
Response Rate Limiting (RRL) RRL, or Response Rate Limiting, is a security feature implemented in DNS servers to mitigate the impact of Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks, particularly DNS amplification attacks. It works by limiting the ...Response Rate Limiting (RRL)
RRL, or Response Rate Limiting, is a security feature implemented in DNS servers to mitigate the impact of Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks, particularly DNS amplification attacks. It works by limiting the rate at which DNS responses are ...22. Configuring Response Rate Limiting (RRL) settings
Configuring DNS Response Rate Limiting (RRL) settings Response Rate Limiting (RRL) is a security feature designed to mitigate the impact of DNS amplification attacks by limiting the rate of responses a DNS server can send to a client. Configuring RRL ...Configuring DNS client subnets
Configuring DNS Clientsubnets Client subnets in Microsoft DNS, are named groups of IP subnets that allow DNS servers to provide more specific responses based on the client’s location or network segment. A client subnet is identified by a name and ...