[Tips & Tricks] ServiceDesk Plus on Docker


Let’s say you need to Host an application and make it available to the
public, you need someplace to host it. In the past, you would need to host this
on a Dedicated Server or a Physical Computer.
Then, the age of “Virtualization” came in. Hosting
applications on VM became popular due to its advantages like: Easy
maintenance, Multiple OS environments can exist simultaneously on the same
machine, isolated from each other and availability and convenient recovery.
But the above two computing services still cannot solve one thing
— heavy Operating System usage. Let’s think about operating
systems like Windows, Linux (RHEL, Fedora, Ubuntu, etc), and macOS. These OS
s are large in size and can easily go over 1 Gigabyte, also known as “OS
image.”
However, your application may only have an approximated size of 300 MB
to start with. So, why would you want a “virtual machine”that has the size of 1
GB + when your application is much much less than that? That’s where the
concept of “container” comes in to fix that.
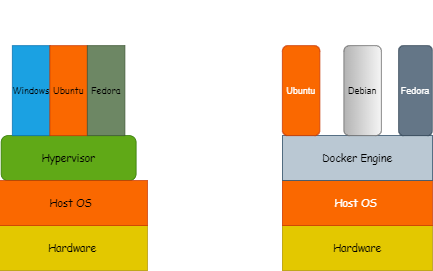
Is this the only issue Docker solves? Definitely No,
the picture below explains it all!

The application works fine in our Laptop, but it doesn't work on
Production server or a user's machine due to the difference in computing the environment between the two.
Docker is a platform that packages an application and all its
dependencies together in the form of containers. This containerization aspect
of Docker ensures that the application works in any environment.
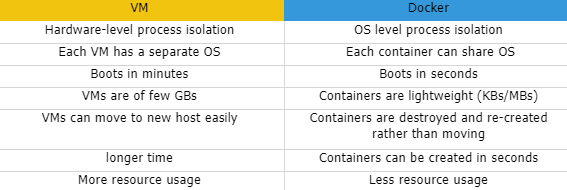
Instructions to Install SDP on Docker (Attached a
Word and Pdf doc)
2)Download ServiceDeskplus .bin for Linux on the host
machine ( Windows) from: https://www.manageengine.com/products/service-desk/download.html?opDownload_indexbnr
3)Create a folder “SDP” and move the .bin file
Here, this will help to share the folder with the
docker container.
For illustration, we have used CentOS image on
Docker. However, the steps remain the same for other Linux distributions like
Ubuntu, Fedora, and Debian. etc.
Docker: 19.03.8
Host OS: Windows 10
Container : CentOS:7
Once Docker is installed and running,
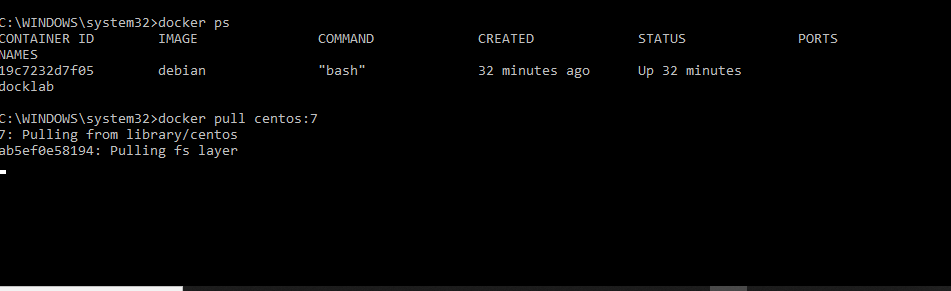
Command to install centos on this container :
Docker pull centos:7
This will pull an image of the centos7 from Docker Hub and create the
container required to host applications on this Centos.
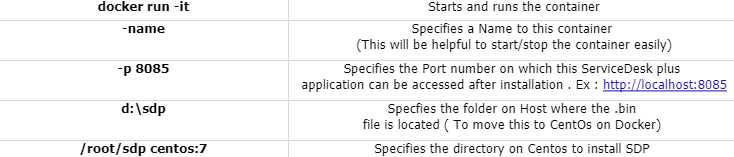
Step 2 : Give a name to this container and start
the container
Command :
docker run -it —name sdp -p 8085:8080 -v d:\sdp:/root/sdp centos:7
bin/bash

Type ls to find the bin file for
installation
./ManageEngine_ServiceDesk_Plus_64bits.bin --console
Give the permission for execution with ‘chmod +x’
Run the command as shown below
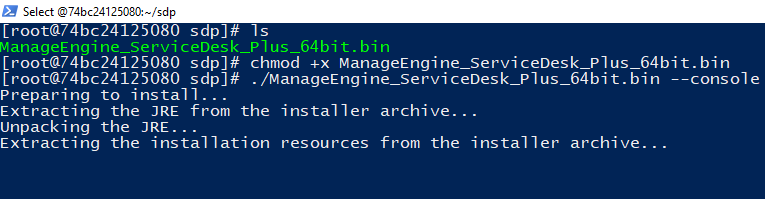
From this stage, the installation
steps remain the same as how we normally install SDP on Linux as mentioned https://help.servicedeskplus.com/introduction/installation-linux.html
Continue the Onscreen instructions to proceed and in case if you
encounter an error as shown below- it is safe to ignore.
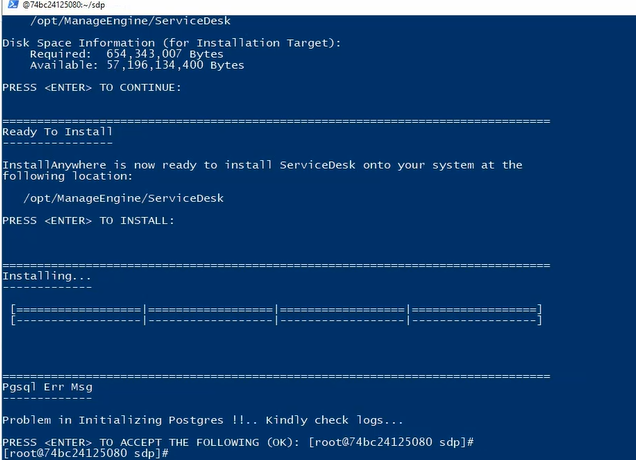
Step 4: Start
ServiceDesk plus:
Command : ./run.sh
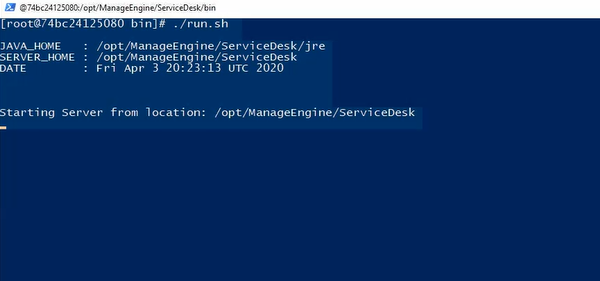
Step 5 : Configuring
ServiceDesk plus as a Service
Create a file inside /etc/init.d/
Command :$ touch /etc/init.d/servicedesk
Give permission for execution
Command :chmod 755 /etc/init.d/servicedesk
Access the startup script from: https://help.servicedeskplus.com/servicedesk.txt
open the file with your text editor, nano, emacs, vim, etc…
copy the contents and paste it on the newly created file
$ nano /etc/init.d/servicedesk
Change this line
.MDIR=/home/guest/servicedesk/AdventNet/ME/ServiceDesk/bin
To
.MDIR=/opt/ManageEngine/ServiceDesk/bin
Now save the file.
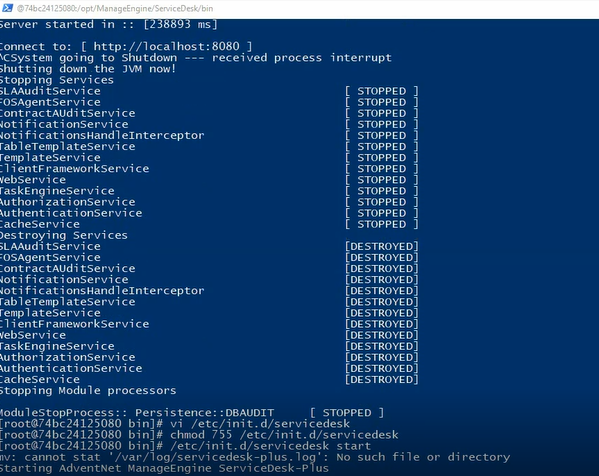
Now you can start Service desk plus using the
command : $ /etc/init.d/servicedesk start
To exit the container without stopping it - use : Ctlr + p and q
Do not use Control D or the command #exit since
this will stop the container.
Few useful Docker commands:
To start a container
docker start <containername>
To login to the container
docker attach <container_name>
To stop the container
$ docker <container_name> or <container_id> stop
To remove a container
$ docker rm <container_name> or <container_id>